React Native 鸿蒙跨平台开发:useContext 和 useReducer 代码指南
一、核心知识点:useContext 和 useReducer 完整核心用法
1. 用到的纯内置组件与 API
所有能力均为 RN 原生自带,全部从 react 核心包直接导入,无任何额外依赖、无任何第三方库,鸿蒙端无任何兼容问题,也是实现 useContext 和 useReducer 的全部核心能力,零基础易理解、易复用,无任何冗余,所有 useContext 和 useReducer 功能均基于以下组件/API 原生实现:
| useContext | React 原生钩子,读取 Context 值,实现跨组件状态共享 | ✅ 鸿蒙端 Context 读取正常,无兼容问题 |
| useReducer | React 原生钩子,管理复杂状态逻辑,替代 useState | ✅ 鸿蒙端状态管理正常,无兼容问题 |
| createContext | React 原生函数,创建 Context 对象 | ✅ 鸿蒙端 Context 创建正常,无兼容问题 |
| Context.Provider | Context 提供者组件,提供 Context 值 | ✅ 鸿蒙端 Provider 正常工作 |
| View | 核心容器组件,实现所有「状态显示容器、交互容器」,支持圆角、背景色、阴影 | ✅ 鸿蒙端样式渲染无错位,宽高、圆角、背景色属性完美生效 |
| Text | 文本组件,显示状态信息和计数 | ✅ 鸿蒙端文本渲染正常,支持多行文本 |
| TextInput | 输入框组件,实现用户输入和状态更新 | ✅ 鸿蒙端输入框正常工作,支持键盘类型 |
| TouchableOpacity | 触摸反馈组件,实现状态修改交互 | ✅ 鸿蒙端触摸响应正常,交互流畅 |
| StyleSheet | 原生样式管理,编写鸿蒙端最优的 useContext 和 useReducer 样式:状态显示样式、按钮样式,无任何不兼容CSS属性 | ✅ 贴合鸿蒙官方视觉设计规范,颜色、圆角、间距均为真机实测最优值 |
| SafeAreaView | 安全区域容器,适配刘海屏等异形屏 | ✅ 鸿蒙端安全区域适配正常 |
二、深入理解 useContext
1. useContext 是什么?
useContext 是 React 提供的一个 Hook,用于读取 Context 的值。它让你能够订阅 Context 的变化,并在 Context 值变化时重新渲染组件。
2. 为什么需要 useContext?
在 React 中,当组件层级很深时,通过 props 逐层传递数据会变得非常繁琐和难以维护。useContext 提供了一种跨组件状态共享的解决方案,允许你在组件树的任何位置访问和更新状态,而无需通过 props 逐层传递。
3. useContext 的基本语法
const value = useContext(MyContext);
参数说明:
- MyContext:通过 createContext 创建的 Context 对象
返回值:
- 返回当前 Context 的值
4. useContext 的工作原理
当你调用 useContext(MyContext) 时,React 会:
5. useContext 的类型定义
function useContext<T>(context: Context<T>): T;
这个定义告诉我们:
- useContext 接受一个泛型参数 T,表示 Context 值的类型
- context:通过 createContext<T> 创建的 Context 对象
- 返回值:类型为 T 的值
6. useContext 的使用场景
useContext 适用于以下场景:
- 跨组件状态共享:在组件树的任何位置访问和更新状态
- 主题切换:实现全局主题切换(如暗黑模式)
- 用户认证:共享用户登录状态
- 国际化:共享语言和地区设置
- 应用配置:共享应用配置信息
- 全局状态管理:替代 Redux 等状态管理库
7. useContext 的最佳实践
✅ 最佳实践 1:正确创建和使用 Context
// 创建 Context
const ThemeContext = createContext({
theme: 'light',
toggleTheme: () => {},
});
// 创建 Provider 组件
const ThemeProvider = ({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('light');
const toggleTheme = useCallback(() => {
setTheme(prev => prev === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light');
}, []);
const value = {
theme,
toggleTheme,
};
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={value}>
{children}
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
};
// 使用 Context
const ThemedComponent = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<View style={{ backgroundColor: theme === 'light' ? '#FFFFFF' : '#000000' }}>
<Text style={{ color: theme === 'light' ? '#000000' : '#FFFFFF' }}>
当前主题: {theme}
</Text>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={toggleTheme}>
<Text>切换主题</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
);
};
原因:
- 将状态和方法一起放在 Context 中
- 使用 Provider 包裹应用
- 在需要的组件中使用 useContext
✅ 最佳实践 2:避免过度使用 Context
// ❌ 不推荐:将所有状态都放在 Context 中
const AppContext = createContext({
user: null,
posts: [],
comments: [],
settings: {},
// … 更多状态
});
// ✅ 推荐:按功能拆分 Context
const UserContext = createContext({ user: null, login: () => {}, logout: () => {} });
const PostsContext = createContext({ posts: [], addPost: () => {}, removePost: () => {} });
const CommentsContext = createContext({ comments: [], addComment: () => {} });
原因:
- 避免不必要的重新渲染
- 更好的代码组织
- 更容易维护
✅ 最佳实践 3:使用自定义 Hook 封装 Context
// ❌ 不推荐:在每个组件中都使用 useContext
const Component1 = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
// …
};
const Component2 = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
// …
};
// ✅ 推荐:使用自定义 Hook 封装
const useTheme = () => {
const context = useContext(ThemeContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error('useTheme must be used within a ThemeProvider');
}
return context;
};
const Component1 = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useTheme();
// …
};
const Component2 = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useTheme();
// …
};
原因:
- 更清晰的代码结构
- 避免重复代码
- 类型安全
三、深入理解 useReducer
1. useReducer 是什么?
useReducer 是 React 提供的一个 Hook,用于管理复杂状态逻辑。它是 useState 的替代方案,适用于状态逻辑比较复杂或下一个状态依赖于前一个状态的场景。
2. 为什么需要 useReducer?
在 React 中,当状态逻辑比较复杂时,使用 useState 会导致代码变得难以理解和维护。useReducer 提供了一种将状态更新逻辑集中管理的方式,使代码更加清晰和可维护。
useReducer 的优势包括:
3. useReducer 的基本语法
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
参数说明:
- reducer:reducer 函数,接受当前状态和 action,返回新状态
- initialState:初始状态
返回值:
- state:当前状态
- dispatch:dispatch 函数,用于触发状态更新
4. useReducer 的工作原理
当你调用 useReducer(reducer, initialState) 时,React 会:
- 调用 reducer 函数,传入当前状态和 action
- 根据 action 类型计算新状态
- 更新状态并重新渲染组件
5. useReducer 的类型定义
function useReducer<R extends Reducer<any, any>, I>(
reducer: R,
initialState: I & ReducerState<R>,
initializer?: undefined
): [I & ReducerState<R>, Dispatch<ReducerAction<R>>];
这个定义告诉我们:
- useReducer 接受一个泛型参数 R,表示 reducer 函数的类型
- reducer:reducer 函数,类型为 Reducer<any, any>
- initialState:初始状态
- initializer:可选的初始化函数
- 返回值:一个元组,包含状态和 dispatch 函数
6. useReducer 的使用场景
useReducer适用于以下场景:
- 复杂状态逻辑:状态更新逻辑比较复杂
- 多个相关状态:多个状态之间有依赖关系
- 下一个状态依赖于前一个状态:如计数器、购物车等
- 状态更新模式:有固定的状态更新模式
- 可预测的状态更新:需要可预测的状态更新
7. useReducer 的最佳实践
✅ 最佳实践 1:正确定义 action 类型
// ❌ 不推荐:使用字符串作为 action 类型
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action) {
case 'increment':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement':
return { count: state.count – 1 };
default:
return state;
}
};
// ✅ 推荐:使用对象作为 action 类型
type CounterAction =
| { type: 'increment' }
| { type: 'decrement' }
| { type: 'reset' }
| { type: 'setCount'; value: number };
const reducer = (state: CounterState, action: CounterAction): CounterState => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement':
return { count: state.count – 1 };
case 'reset':
return { count: 0 };
case 'setCount':
return { count: action.value };
default:
return state;
}
};
原因:
- 类型安全
- 更好的 IDE 支持
- 避免拼写错误
✅ 最佳实践 2:正确使用 dispatch
// ❌ 不推荐:直接修改状态
const handleIncrement = () => {
setState(prev => ({ …prev, count: prev.count + 1 }));
};
// ✅ 推荐:使用 dispatch 触发状态更新
const handleIncrement = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'increment' });
};
原因:
- 状态更新逻辑集中在 reducer 中
- 更好的可维护性
- 更容易调试
✅ 最佳实践 ③:拆分复杂 reducer
// ❌ 不推荐:一个 reducer 处理所有逻辑
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { …state, count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement':
return { …state, count: state.count – 1 };
case 'addItem':
return { …state, items: […state.items, action.item] };
case 'removeItem':
return { …state, items: state.items.filter(item => item.id !== action.id) };
case 'updateItem':
return { …state, items: state.items.map(item => item.id === action.id ? action.item : item) };
// … 更多 case
default:
return state;
}
};
// ✅ 推荐:拆分成多个 reducer
const counterReducer = (state: CounterState, action: CounterAction): CounterState => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { …state, count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement':
return { …state, count: state.count – 1 };
case 'reset':
return { count: 0 };
case 'setCount':
return { count: action.value };
default:
return state;
}
};
const itemsReducer = (state: ItemsState, action: ItemsAction): ItemsState => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'addItem':
return { …state, items: […state.items, action.item] };
case 'removeItem':
return { …state, items: state.items.filter(item => item.id !== action.id) };
case 'updateItem':
return { …state, items: state.items.map(item => item.id === action.id ? action.item : item) };
default:
return state;
}
};
// 使用 combineReducers 合并 reducer
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
counter: counterReducer,
items: itemsReducer,
});
原因:
- 更清晰的代码结构
- 更容易维护
- 更容易测试
四、实战完整版:企业级通用 useContext 和 useReducer
import React, { useState, useReducer, useCallback, useContext, createContext, useEffect } from 'react';
import {
View,
Text,
StyleSheet,
TouchableOpacity,
SafeAreaView,
ScrollView,
TextInput,
FlatList,
} from 'react-native';
// ========== Context 定义 ==========
// 主题 Context
type Theme = 'light' | 'dark';
interface ThemeContextType {
theme: Theme;
toggleTheme: () => void;
}
const ThemeContext = createContext<ThemeContextType>({
theme: 'light',
toggleTheme: () => {},
});
// 用户 Context
interface User {
id: string;
name: string;
email: string;
}
interface AuthContextType {
user: User | null;
isAuthenticated: boolean;
isLoading: boolean;
error: string | null;
login: (username: string, password: string) => Promise<void>;
logout: () => void;
}
const AuthContext = createContext<AuthContextType>({
user: null,
isAuthenticated: false,
isLoading: false,
error: null,
login: async () => {},
logout: () => {},
});
// ========== Reducer 定义 ==========
// 计数器 Reducer
interface CounterState {
count: number;
history: number[];
}
type CounterAction =
| { type: 'increment' }
| { type: 'decrement' }
| { type: 'reset' }
| { type: 'setCount'; value: number };
const counterReducer = (state: CounterState, action: CounterAction): CounterState => {
let newCount: number;
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
newCount = state.count + 1;
return {
count: newCount,
history: […state.history, newCount],
};
case 'decrement':
newCount = state.count – 1;
return {
count: newCount,
history: […state.history, newCount],
};
case 'reset':
return { count: 0, history: [] };
case 'setCount':
return {
count: action.value,
history: […state.history, action.value],
};
default:
return state;
}
};
// 表单 Reducer
interface FormState {
values: Record<string, string>;
errors: Record<string, string>;
touched: Record<string, boolean>;
isValid: boolean;
}
type FormAction =
| { type: 'setValue'; field: string; value: string }
| { type: 'setError'; field: string; error: string }
| { type: 'setTouched'; field: string; touched: boolean }
| { type: 'reset' };
const formReducer = (state: FormState, action: FormAction): FormState => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'setValue':
return {
…state,
values: { …state.values, [action.field]: action.value },
};
case 'setError':
return {
…state,
errors: { …state.errors, [action.field]: action.error },
};
case 'setTouched':
return {
…state,
touched: { …state.touched, [action.field]: action.touched },
};
case 'reset':
return {
values: {},
errors: {},
touched: {},
isValid: true,
};
default:
return state;
}
};
// ========== Provider 组件 ==========
const AppProvider = ({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) => {
// 主题状态
const [theme, setTheme] = useState<Theme>('light');
const toggleTheme = useCallback(() => {
setTheme(prev => prev === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light');
}, []);
const themeValue: ThemeContextType = {
theme,
toggleTheme,
};
// 认证状态
const [user, setUser] = useState<User | null>(null);
const [isAuthenticated, setIsAuthenticated] = useState(false);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState<string | null>(null);
const login = useCallback(async (username: string, password: string) => {
setIsLoading(true);
setError(null);
try {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
if (username === 'admin' && password === '123456') {
setUser({ id: '1', name: '管理员', email: 'admin@example.com' });
setIsAuthenticated(true);
} else {
setError('用户名或密码错误');
}
} catch (err) {
setError('登录失败,请稍后重试');
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
}, []);
const logout = useCallback(() => {
setUser(null);
setIsAuthenticated(false);
setError(null);
}, []);
const authValue: AuthContextType = {
user,
isAuthenticated,
isLoading,
error,
login,
logout,
};
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={themeValue}>
<AuthContext.Provider value={authValue}>
{children}
</AuthContext.Provider>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
};
// ========== 自定义 Hook ==========
const useTheme = () => {
const context = useContext(ThemeContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error('useTheme must be used within AppProvider');
}
return context;
};
const useAuth = () => {
const context = useContext(AuthContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error('useAuth must be used within AppProvider');
}
return context;
};
// ========== 示例组件 ==========
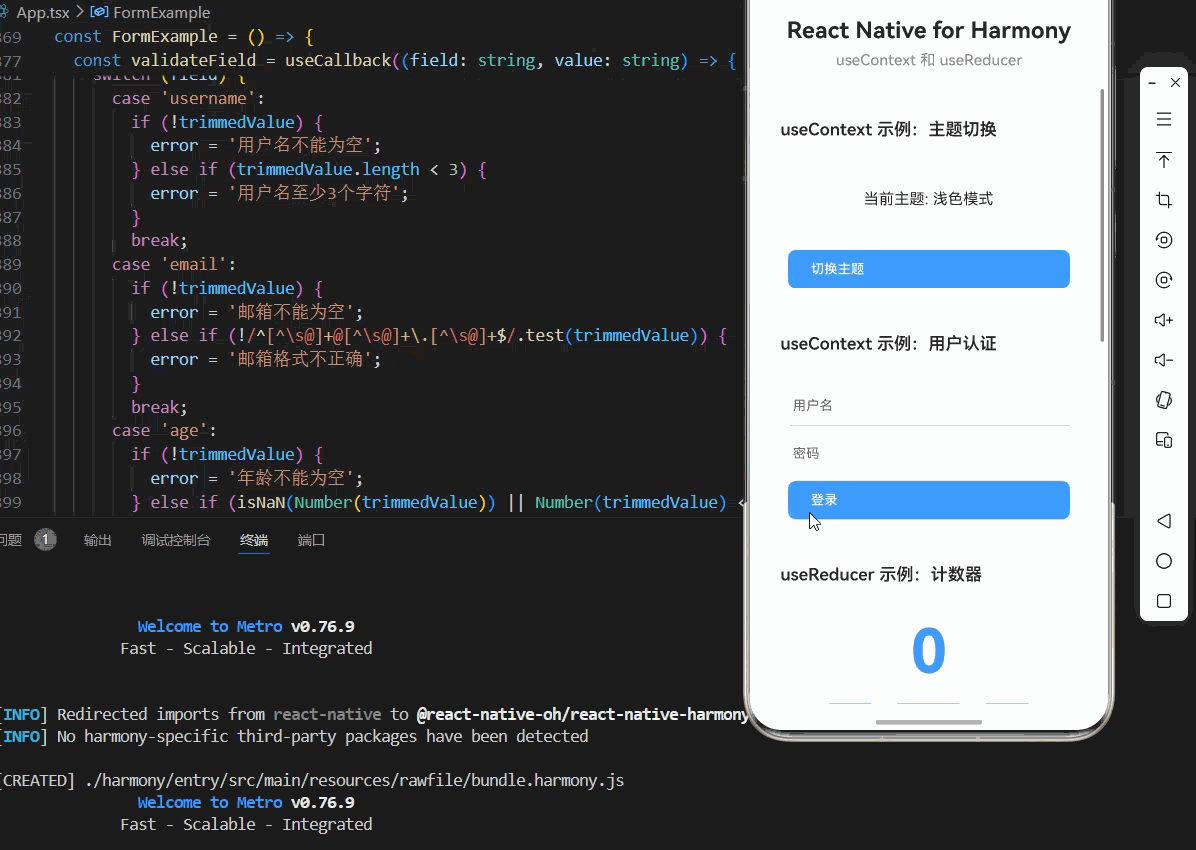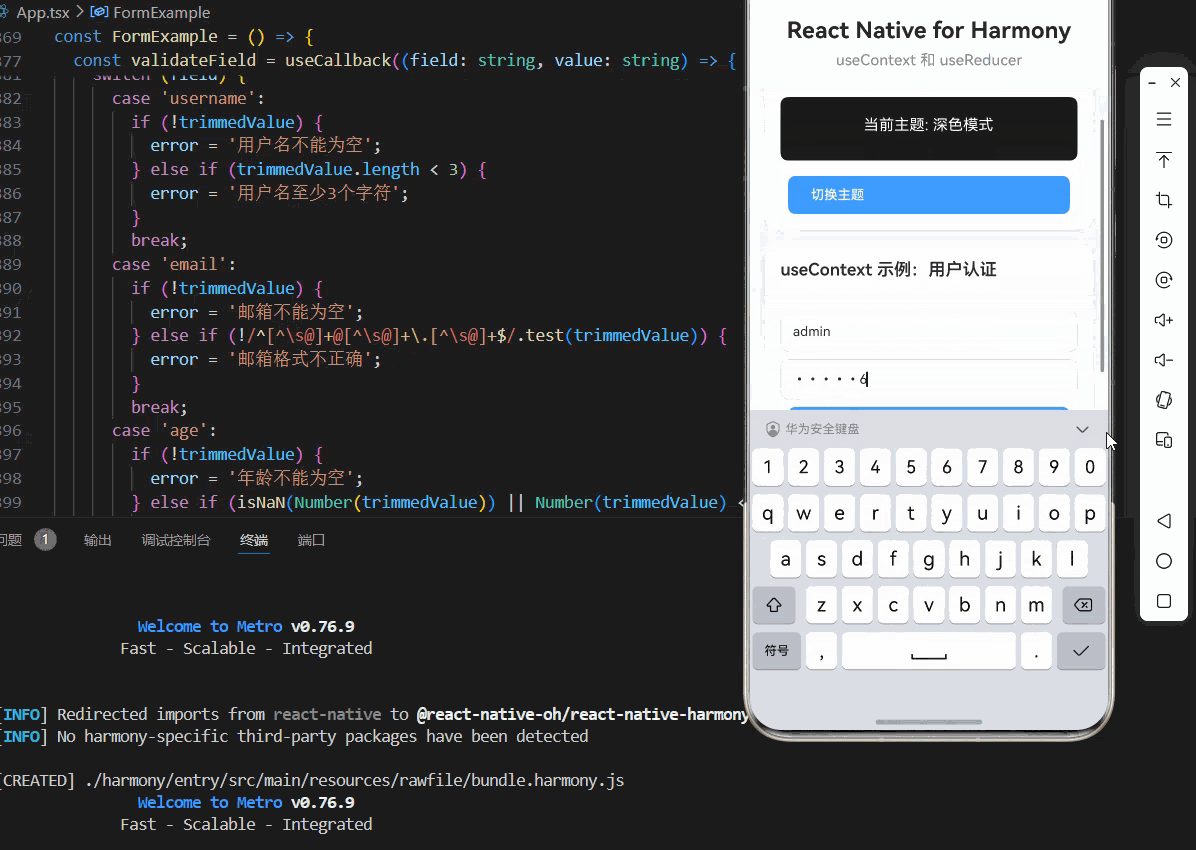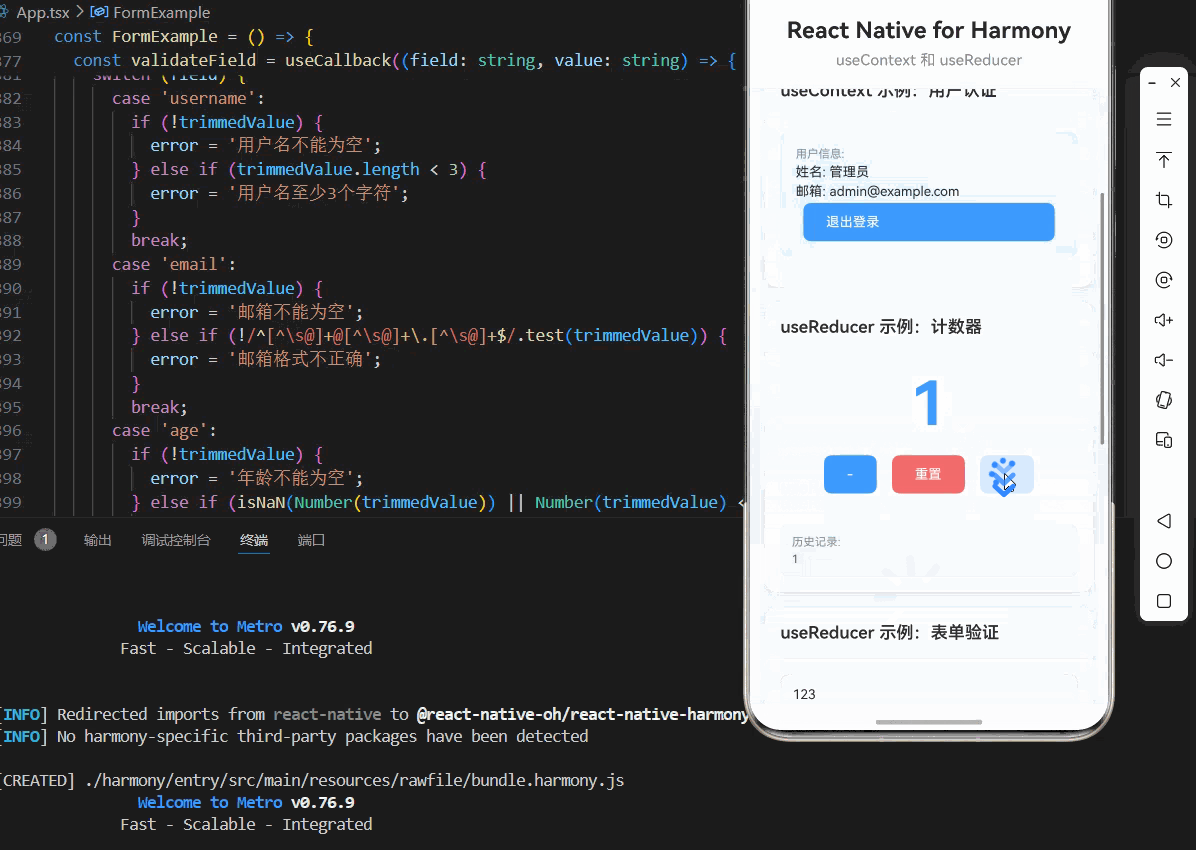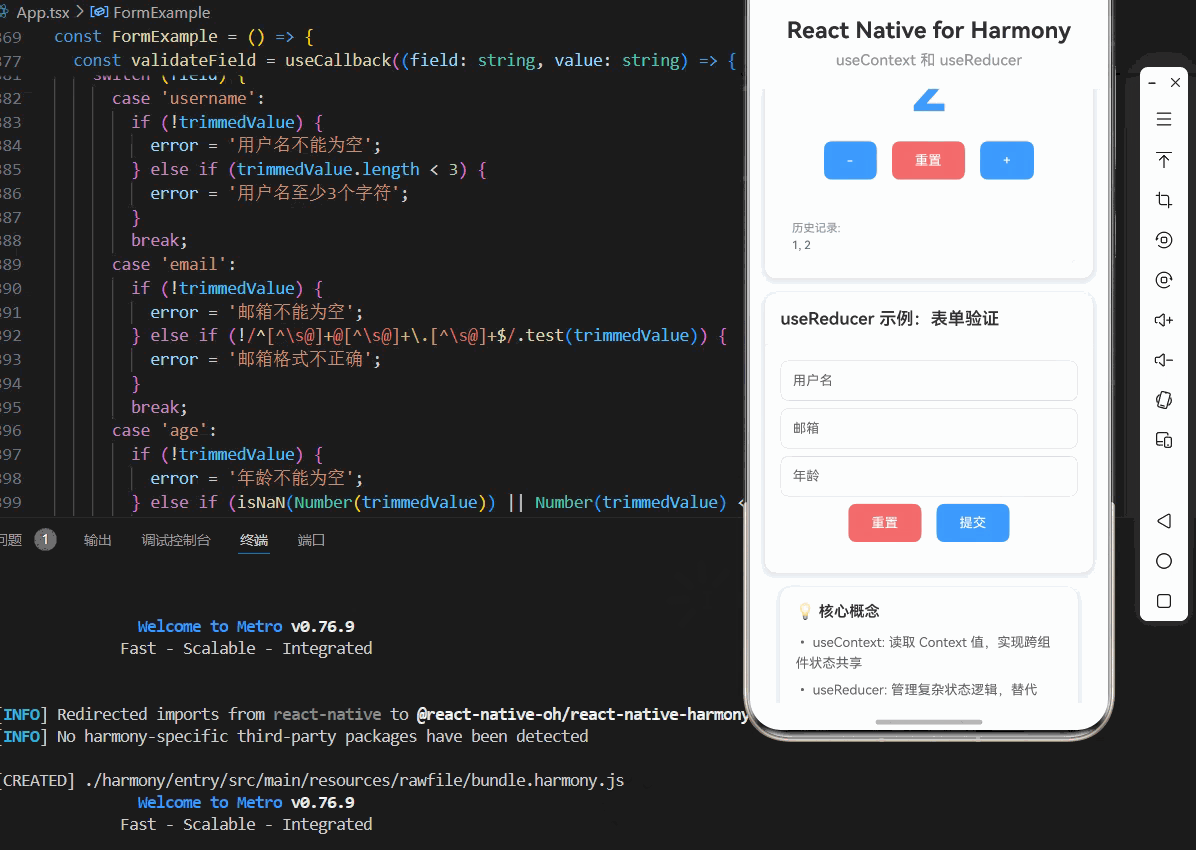
// useContext 示例:主题切换
const ThemeExample = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useTheme();
return (
<View style={styles.card}>
<View style={styles.cardHeader}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>useContext 示例:主题切换</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.cardBody}>
<View style={[
styles.themePreview,
theme === 'dark' ? styles.darkThemePreview : null,
]}>
<Text style={[
styles.themeText,
theme === 'dark' ? styles.darkThemeText : null,
]}>
当前主题: {theme === 'light' ? '浅色模式' : '深色模式'}
</Text>
</View>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={toggleTheme}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>切换主题</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</View>
);
};
// useContext 示例:用户认证
const AuthExample = () => {
const { user, isAuthenticated, isLoading, error, login, logout } = useAuth();
const [username, setUsername] = useState('');
const [password, setPassword] = useState('');
const handleLogin = useCallback(async () => {
await login(username, password);
}, [login, username, password]);
return (
<View style={styles.card}>
<View style={styles.cardHeader}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>useContext 示例:用户认证</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.cardBody}>
{isAuthenticated ? (
<View style={styles.authInfo}>
<Text style={styles.authLabel}>用户信息:</Text>
<Text style={styles.authValue}>姓名: {user?.name}</Text>
<Text style={styles.authValue}>邮箱: {user?.email}</Text>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={logout}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>退出登录</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
) : (
<>
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
placeholder="用户名"
value={username}
onChangeText={setUsername}
/>
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
placeholder="密码"
value={password}
onChangeText={setPassword}
secureTextEntry
/>
{error && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{error}</Text>}
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={handleLogin}
disabled={isLoading}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>
{isLoading ? '登录中…' : '登录'}
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</>
)}
</View>
</View>
);
};
// useReducer 示例:计数器
const CounterExample = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(counterReducer, {
count: 0,
history: [],
});
const increment = useCallback(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'increment' });
}, []);
const decrement = useCallback(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'decrement' });
}, []);
const reset = useCallback(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'reset' });
}, []);
const setCount = useCallback((value: number) => {
dispatch({ type: 'setCount', value });
}, []);
return (
<View style={styles.card}>
<View style={styles.cardHeader}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>useReducer 示例:计数器</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.cardBody}>
<Text style={styles.countText}>{state.count}</Text>
<View style={styles.buttonRow}>
<TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={decrement}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>–</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<TouchableOpacity
style={[styles.button, styles.resetButton]}
onPress={reset}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>重置</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={increment}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>+</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<View style={styles.historyContainer}>
<Text style={styles.historyLabel}>历史记录:</Text>
<Text style={styles.historyValue}>{state.history.join(', ') || '无'}</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
};
// useReducer 示例:表单验证
const FormExample = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(formReducer, {
values: {},
errors: {},
touched: {},
isValid: true,
});
const validateField = useCallback((field: string, value: string) => {
let error = '';
const trimmedValue = value ? value.trim() : '';
switch (field) {
case 'username':
if (!trimmedValue) {
error = '用户名不能为空';
} else if (trimmedValue.length < 3) {
error = '用户名至少3个字符';
}
break;
case 'email':
if (!trimmedValue) {
error = '邮箱不能为空';
} else if (!/^[^\\s@]+@[^\\s@]+\\.[^\\s@]+$/.test(trimmedValue)) {
error = '邮箱格式不正确';
}
break;
case 'age':
if (!trimmedValue) {
error = '年龄不能为空';
} else if (isNaN(Number(trimmedValue)) || Number(trimmedValue) < 0) {
error = '年龄必须是正数';
}
break;
}
dispatch({ type: 'setError', field, error });
}, []);
const handleChange = useCallback((field: string, value: string) => {
dispatch({ type: 'setValue', field, value });
// 实时验证,输入时清除错误
if (value && value.trim() !== '') {
validateField(field, value);
}
}, [validateField]);
const handleBlur = useCallback((field: string) => {
dispatch({ type: 'setTouched', field, touched: true });
// 使用当前输入的值进行验证
const currentValue = state.values[field] || '';
validateField(field, currentValue);
}, [state.values, validateField]);
const validate = useCallback(() => {
const newErrors: Record<string, string> = {};
Object.keys(state.values).forEach(field => {
validateField(field, state.values[field]);
});
const isValid = Object.keys(newErrors).length === 0;
dispatch({ type: 'reset' });
return isValid;
}, [state.values, validateField]);
const handleSubmit = useCallback(() => {
if (validate()) {
console.log('提交表单:', state.values);
alert('提交成功!');
}
}, [state.values, validate]);
const handleReset = useCallback(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'reset' });
}, []);
return (
<View style={styles.card}>
<View style={styles.cardHeader}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>useReducer 示例:表单验证</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.cardBody}>
<TextInput
style={[styles.input, state.errors.username ? styles.inputError : null]}
placeholder="用户名"
value={state.values.username || ''}
onChangeText={(text) => handleChange('username', text)}
onBlur={() => handleBlur('username')}
/>
{state.errors.username && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{state.errors.username}</Text>}
<TextInput
style={[styles.input, state.errors.email ? styles.inputError : null]}
placeholder="邮箱"
value={state.values.email || ''}
onChangeText={(text) => handleChange('email', text)}
onBlur={() => handleBlur('email')}
/>
{state.errors.email && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{state.errors.email}</Text>}
<TextInput
style={[styles.input, state.errors.age ? styles.inputError : null]}
placeholder="年龄"
value={state.values.age || ''}
onChangeText={(text) => handleChange('age', text)}
onBlur={() => handleBlur('age')}
keyboardType="numeric"
/>
{state.errors.age && <Text style={styles.errorText}>{state.errors.age}</Text>}
<View style={styles.buttonRow}>
<TouchableOpacity
style={[styles.button, styles.resetButton]}
onPress={handleReset}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>重置</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.button}
onPress={handleSubmit}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>提交</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
};
// 主界面
const UseContextUseReducerScreen = () => {
return (
<AppProvider>
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
{/* 标题区域 */}
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.pageTitle}>React Native for Harmony</Text>
<Text style={styles.subtitle}>useContext 和 useReducer</Text>
</View>
{/* 内容区域 */}
<ScrollView style={styles.content}>
<ThemeExample />
<AuthExample />
<CounterExample />
<FormExample />
{/* 说明区域 */}
<View style={styles.infoCard}>
<Text style={styles.infoTitle}>💡 核心概念</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• useContext: 读取 Context 值,实现跨组件状态共享</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• useReducer: 管理复杂状态逻辑,替代 useState</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• Context: 创建 Context 对象,提供全局状态</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• Provider: 提供 Context 值,包裹应用组件树</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• Reducer: 集中管理状态更新逻辑</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• Dispatch: 触发状态更新,基于 action 类型</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• 自定义 Hook: 封装 Context 和 useReducer 逻辑</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>• 鸿蒙端完美兼容,性能优秀</Text>
</View>
</ScrollView>
</SafeAreaView>
</AppProvider>
);
};
const App = () => {
return <UseContextUseReducerScreen />;
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#F5F7FA',
},
// ======== 标题区域 ========
header: {
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#EBEEF5',
},
pageTitle: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#303133',
textAlign: 'center',
marginBottom: 8,
},
subtitle: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: '500',
color: '#909399',
textAlign: 'center',
},
// ======== 内容区域 ========
content: {
flex: 1,
padding: 16,
},
// ======== 卡片样式 ========
card: {
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF',
borderRadius: 12,
marginBottom: 16,
shadowColor: '#000000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 8,
elevation: 4,
},
cardHeader: {
padding: 16,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#EBEEF5',
},
cardTitle: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: '600',
color: '#303133',
},
cardBody: {
padding: 16,
},
// ======== 主题样式 ========
themePreview: {
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 20,
marginBottom: 16,
alignItems: 'center',
},
darkThemePreview: {
backgroundColor: '#1a1a1a',
},
themeText: {
fontSize: 16,
color: '#303133',
marginBottom: 8,
},
darkThemeText: {
color: '#FFFFFF',
},
// ======== 认证信息样式 ========
authInfo: {
backgroundColor: '#E6F7FF',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 16,
marginBottom: 16,
},
authLabel: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#909399',
marginBottom: 4,
},
authValue: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#303133',
marginBottom: 4,
},
// ======== 计数器样式 ========
countText: {
fontSize: 64,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#409EFF',
textAlign: 'center',
marginBottom: 16,
},
historyContainer: {
backgroundColor: '#F5F7FA',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 12,
marginTop: 16,
},
historyLabel: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#909399',
marginBottom: 4,
},
historyValue: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#606266',
},
// ======== 输入框样式 ========
input: {
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: '#DCDFE6',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 12,
fontSize: 14,
color: '#303133',
marginBottom: 8,
},
inputError: {
borderColor: '#F56C6C',
},
// ======== 按钮样式 ========
buttonRow: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'center',
marginBottom: 16,
},
button: {
backgroundColor: '#409EFF',
paddingHorizontal: 24,
paddingVertical: 12,
borderRadius: 8,
marginHorizontal: 8,
},
resetButton: {
backgroundColor: '#F56C6C',
},
buttonText: {
color: '#FFFFFF',
fontSize: 14,
fontWeight: '500',
},
// ======== 错误文本 ========
errorText: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#F56C6C',
marginBottom: 8,
},
// ======== 信息卡片 ========
infoCard: {
backgroundColor: '#FFFFFF',
borderRadius: 12,
padding: 16,
margin: 16,
marginTop: 0,
shadowColor: '#000000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 8,
elevation: 4,
},
infoTitle: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: '600',
color: '#303133',
marginBottom: 12,
},
infoText: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#606266',
lineHeight: 22,
marginBottom: 6,
},
});
export default App;
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心




评论前必须登录!
注册