引入
并查集(Disjoint Set Union,DSU)是一种用于管理元素分组的数据结构。
合并(Union):将两个不相交的集合合并为一个集合。
查找(Find):确定某个元素属于哪个集合,通常通过返回集合的“代表元素”(groupID或父节点)实现。
quickFind 和 quickUnion 是并查集的两种实现方式。
每个元素初始时是一个独立的集合,其groupID是本身下标或父节点指向自己(分别表明各自属于哪个集合)。
如下:
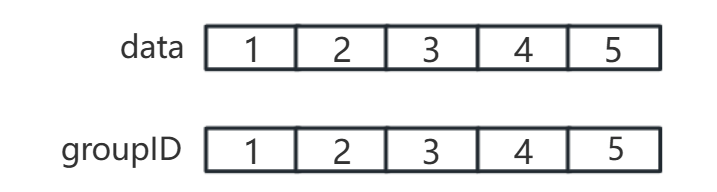
主要就是对两个数组所存的内容进行操作,特别是代表元素部分。
对代表元素进行操作的方向(思考角度)不同,就会使用不同的解决方案(如选择quickFind还是quickUnion,)
quickFind
每个元素直接指向其所属集合的代表元(根节点),合并操作时需要遍历整个数组更新所有相关元素。
时间复杂度:
查找(Find):O(1),直接访问数组即可确定所属集合。
合并(Union):O(n),需要遍历数组更新所有属于同一集合的元素。
特点:查找速度快,但合并效率低(找快合慢)。

头文件
#pragma once
typedef int Element;
typedef struct {
Element* data; //存储具体数据组编号
int* groupID; //存储组编号
int n; //元素个数
}QuickFindSet;
QuickFindSet* createQuickFindSet(int n);//创建n个元素的quickFind树(快查树)
void releaseQuickFindSet(QuickFindSet* setQF);//释放setQF这个树
void initQuickFindSet(const QuickFindSet* setQF, const Element* data, int n);
//初始化setQF这个含n个结点的快查树,以及data数组的值(groupID数组初始时常以下标为值,依次赋值就行了)
//查,判断两个元素是不是同一个组
int isSameQF(QuickFindSet* setQF, Element a, Element b);
//并,合并两个元素
void unionQF(QuickFindSet* setQF, Element a, Element b);
功能实现
创建
QuickFindSet* createQuickFindSet(int n) {
QuickFindSet* setQF = (QuickFindSet*)malloc(sizeof(QuickFindSet));
if (setQF == NULL) {
printf("setQF malloc failed!\\n");
return NULL;
}
//若申请成功,就传递n的值并继续申请两个数组的空间
setQF->n = n;
setQF->data =(Element*) malloc(sizeof(Element) * n);
setQF->groupID = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
return setQF;
}
释放
void releaseQuickFindSet(QuickFindSet* setQF) {
if (setQF) {
if (setQF->data) {
free(setQF->data);
}
if (setQF->groupID) {
free(setQF->groupID);
}
free(setQF);
}
}
初始化
void initQuickFindSet(const QuickFindSet* setQF, const Element* data, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
setQF->data[i] = data[i];
setQF->groupID[i] = i;
}
}
查找目标值的索引
static int findIndex(const QuickFindSet* setQF, Element e) {
for (int i = 0; i < setQF->n; ++i) {
if (setQF->data[i] == e) {
return i;
}
}
return –1;
}
判断目标值索引对应的组ID是否相同(a、b在不在一个集合)
int isSameQF(QuickFindSet* setQF, Element a, Element b) {
int aIndex = findIndex(setQF, a);
int bIndex = findIndex(setQF, b);
if (aIndex == –1 || bIndex == –1) {
return 0;
}
return setQF->groupID[aIndex] == setQF->groupID[bIndex];
}
合并操作
void unionQF(QuickFindSet* setQF, Element a, Element b) {
int aIndex = findIndex(setQF, a);
int bIndex = findIndex(setQF, b);
//假设把b集合中的元素合并到a集合上
int gID = setQF->groupID[bIndex];//先存下b的组号
for (int i = 0; i < setQF->n; ++i) {
if (setQF->groupID[i] == gID) { //是b组的元素
setQF->groupID[i] = setQF->groupID[aIndex]; //全部组号改为a组的组号
}
}
}
功能调用
void test250808() {
int n = 9;
QuickFindSet* QFSet = createQuickFindSet(n);
Element data[9];
for (int i = 0; sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]); ++i) {
data[i] = i;
}
initQuickFindSet(QFSet, data, n);
unionQF(QFSet, 1, 3);
unionQF(QFSet,3, 2);
unionQF(QFSet, 2, 4);
if (isSameQF(QFSet, 0, 2)) {
printf("Yes\\n");
}
else {
printf("No\\n");
}
unionQF(QFSet, 5, 1);
if (isSameQF(QFSet, 5, 2)) {
printf("Yes\\n");
}
else {
printf("No\\n");
}
releaseQuickFindSet(QFSet);
}
int main() {
test250808();
}
quickUnion
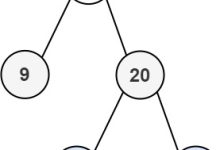
使用树结构表示集合(看下图只能体现链式存储,后面的内容会讲到路径压缩:通过增大节点的度来提高效率会体现出树的特点),每个节点的parent指向其父节点,根节点
的parent指向自身,合并时将一个树的根指向另一个树的根就能连接两个树。
时间复杂度:
查找(Find):O(logn)(平均,取决于树高),需要递归或迭代找到根节点。
合并(Union):O(logn),仅需修改根节点的指向。
特点:合并效率高,但查找速度取决于树高。
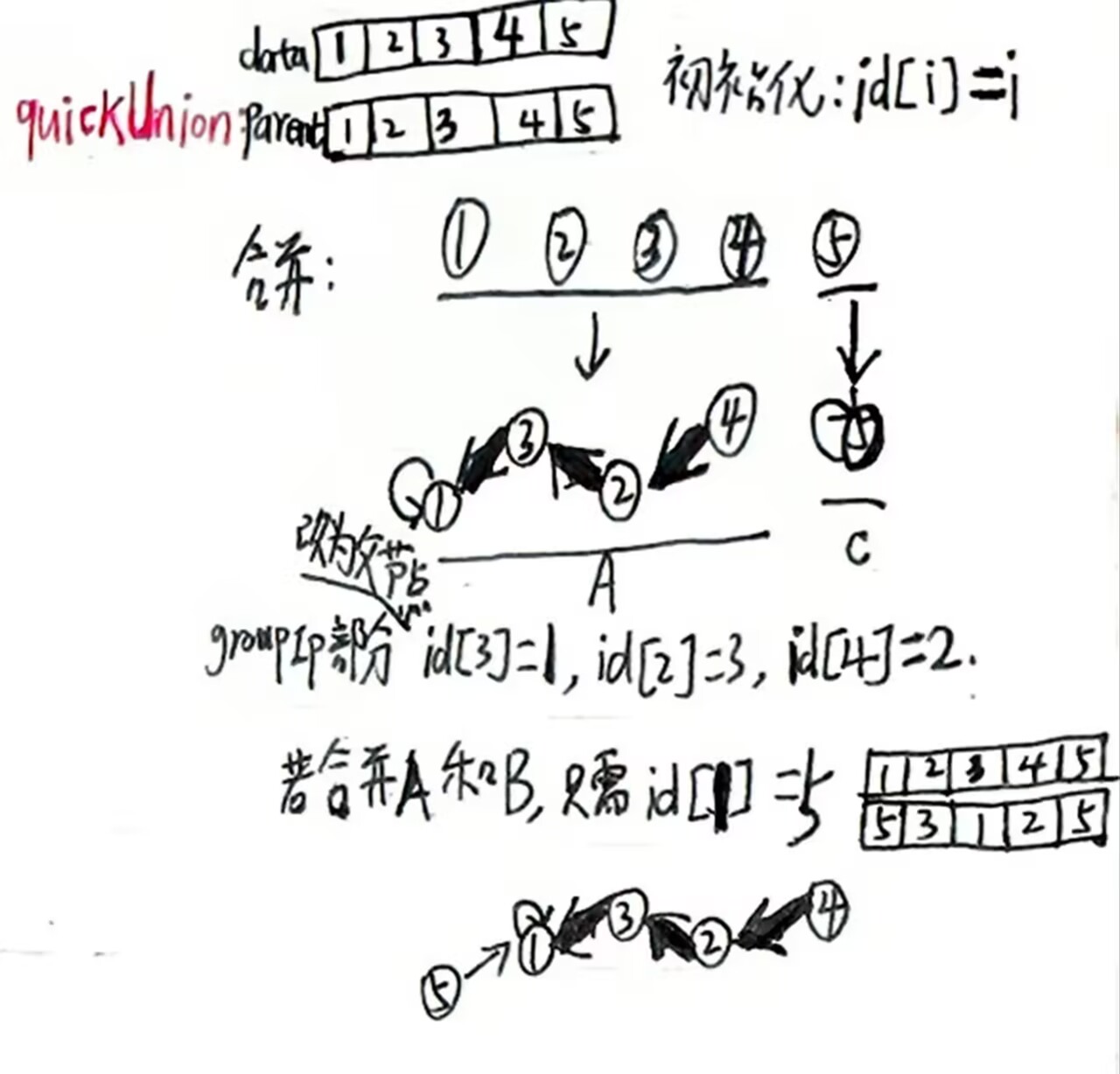
这里是子节点指向父节点;父节点是自己时就指向自己,这种节点被称为根节点(如1和5)。
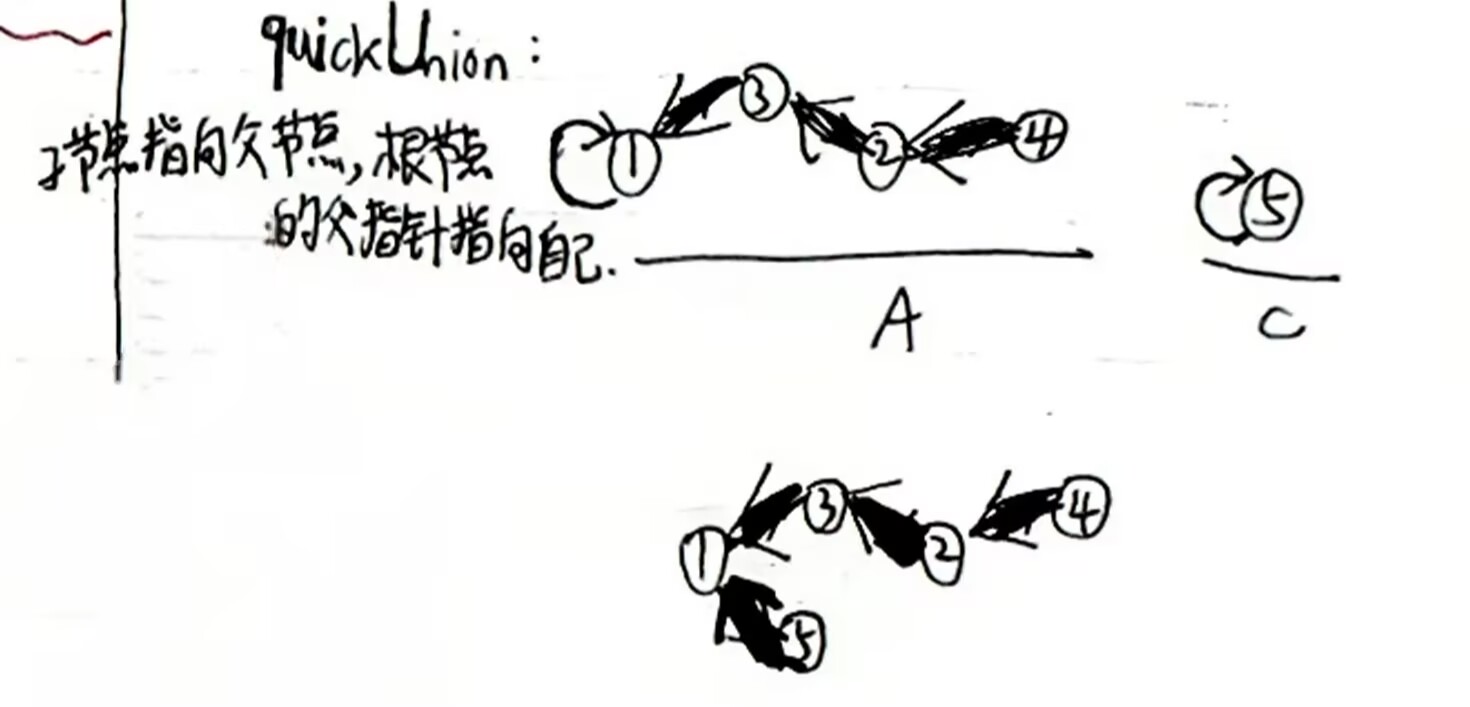
quickUnion查找速度取决于树高,可通过路径压缩等进一步提升性能:
路径压缩
路径压缩就是想办法把树变矮。像上面的例子:从1到4这串右子树,如果从根节点开始往下遍历,将每个节点的parent都直接指向根节点1,当根节点查找目标节点时仅需访问1层。
如何实现这一思想呢?遍历这些节点以及将它们每个节点的parent指向根节点这一环节时,可以想象成从叶子节点开始挨个摘取并存下来(直接指向根节点的叶子节点忽略),遍历到根节点时再挨个取出来并挨个将节点的parent指向根节点。
这种存储特点就不由的联想起了栈,相对提前申请空间的顺序栈,链式栈更合适,用多少就申请多少。且需采用头插法进行入栈操作(方便便利插入节点之后的节点元素)。
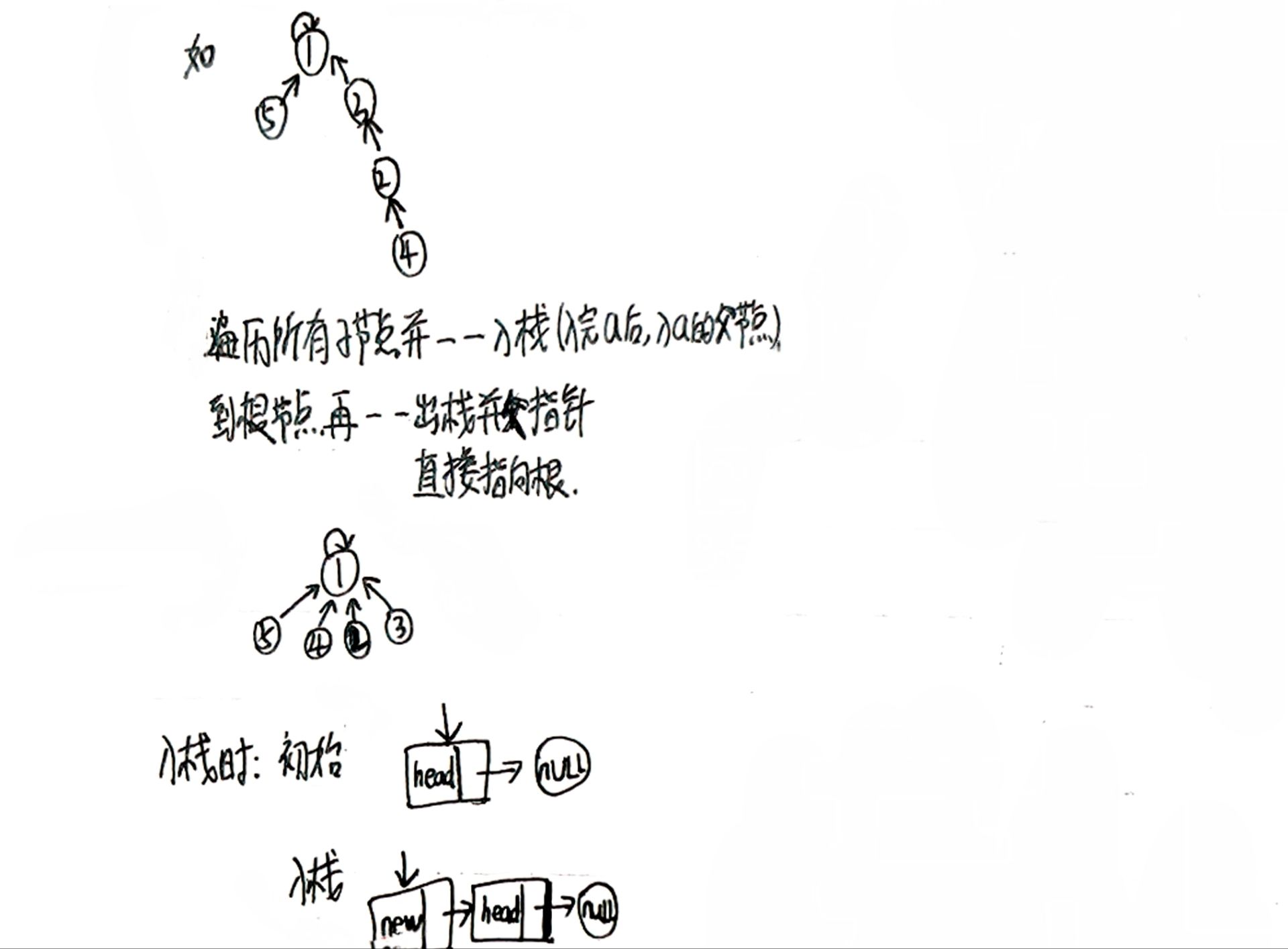
与quickFind的代码很相似,个别地方需调整。
头文件
#pragma once
typedef int Element;
typedef struct {
Element* data;
int* parent;
int* size; //表示其中某个集合的元素个数
int n;//表示总元素个数(所有集合的元素个数之和)
}QuickUnionSet;
//为压缩存储中链式栈的入栈出栈操作做准备:定义节点结构
typedef struct _set_node {
int index;
struct _set_node* next;
}SetNode;
QuickUnionSet* createQuickUnionSet(int n);
void releaseQuickUnionSet(QuickUnionSet* setQU);
void initQuickUnionSet(QuickUnionSet* setQU, const Element* data, int n);
int isSameQU(const QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element a, Element b);
void unionQU(QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element a, Element b);
功能实现
创建
QuickUnionSet* createQuickUnionSet(int n) {
QuickUnionSet* setQU = (QuickUnionSet*)malloc(sizeof(Element) * n);
if (setQU == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
setQU->data = (Element*)malloc(sizeof(Element) * n);
setQU->parent = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
setQU->size = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
setQU->n = n;
return setQU;
}
释放
void releaseQuickUnionSet(QuickUnionSet* setQU) {
if (setQU) {
if (setQU->data) {
free(setQU->data);
}
if (setQU->parent) {
free(setQU->parent);
}
if (setQU->size) {
free(setQU->size);
}
}
}
初始化
void initQuickUnionSet(QuickUnionSet* setQU, const Element* data, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
setQU->data[i] = data[i];
setQU->parent[i] = i;
setQU->size[i] = 1;
}
}
查找目标值索引
static int findIndex(const QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element e) {
for(int i = 0; i < setQU->n; ++i) {
if (setQU->data[i] == e) {
return i;
}
}
return –1;
}
路径压缩
#define PATH_COMPRESS
#ifndef PATH_COMPRESS
static int findRootIndex(const QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element e) {
int curIndex = findIndex(setQU, e);
if (curIndex == –1) {
return –1;
}
//若找到则向上遍历,直到父节点和自身索引一致(找到根节点)
while(setQU->parent[curIndex]!=curIndex) {
curIndex = setQU->parent[curIndex];
}
return curIndex;
}
#else
static SetNode* push(SetNode* stack, int index) {
//传入的stack是一个空指针,相当于无头结点、头指针链式结构的头插操作
SetNode* node = (SetNode*)malloc(sizeof(SetNode));
node->index = index;
node->next = stack;
return node;
}
static SetNode* pop(SetNode* stack, int* index) {
SetNode* tmp = stack;
//主要任务是获得栈顶元素的索引
*index = stack->index;
//之后更新栈顶索引
stack = stack->next;
free(tmp);
return stack;
}
static int findRootIndex(const QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element e) {
int curIndex = findIndex(setQU, e);
if (curIndex == –1)
return –1;
//找根的路径:从目标节点开始往上找,途经的节点都挨个入栈,到根节点为止
SetNode* path = NULL;
while (setQU->parent[curIndex] != curIndex) {
path = push(path, curIndex);
curIndex = setQU->parent[curIndex];
}
//出栈,并将出栈的每个节点的parent都指向根节点
while (path) {
int pos;
path = pop(path, &pos);
setQU->parent[pos] = curIndex;
}
return curIndex;
}
#endif // !PATH_COMPRESS
判断两集合根的异同
int isSameQU(const QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element a, Element b) {
int aRoot = findRootIndex(setQU, a);
int bRoot = findRootIndex(setQU, b);
if (aRoot == –1 || bRoot == –1) {
return 0;
}
return aRoot == bRoot;
}
合并
/* 将元素a和元素b进行合并
* 1. 找到a和b的根节点,原本是b的父节点指向a的父节点
* 2. 引入根节点的size有效规则,谁的元素多,让另外一个接入元素多的组
*/
void unionQU(QuickUnionSet* setQU, Element a, Element b) {
int aRoot = findRootIndex(setQU, a);
int bRoot = findRootIndex(setQU, b);
if (aRoot == –1 || bRoot == –1) {
return;
}
if (aRoot != bRoot) { // a和b不在一个集合里
// 根据根节点的索引找到对应size空间里保存的根所在树的总节点数
//初始时size都为1,节点都是单独占一个集合,结合时再将两集合的size相加
int aSize = setQU->size[aRoot];
int bSize = setQU->size[bRoot];
if (aSize >= bSize) {// 将b元素的根节点指向a元素的根节点
setQU->parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
setQU->size[aRoot] += bSize;
}
else {
setQU->parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
setQU->size[bRoot] += aSize;
}
}
}
功能调用
void test250810() {
int n = 9;
QuickUnionSet* QUSet = createQuickUnionSet(n);
Element data[9];
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]); ++i) {
data[i] = i;
}
initQuickUnionSet(QUSet, data, n);
unionQU(QUSet,1, 3);
unionQU(QUSet, 3, 2);
unionQU(QUSet, 2, 4);
if (isSameQU(QUSet, 0, 2)) {
printf("Yes\\n");
}
else {
printf("No\\n");
}
unionQU(QUSet, 5, 1);
if (isSameQU(QUSet, 5, 2)) {
printf("Yes\\n");
}
else {
printf("No\\n");
}
releaseQuickUnionSet(QUSet);
}
int main() {
test250810();
}
拜拜~
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心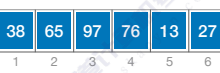




评论前必须登录!
注册