目录
- 一、在本地启动 HTTP 服务器
-
- 1. Windows 下安装 node.js
-
- 1)下载安装包
- 2)配置环境变量
- 3)安装镜像
- 4)node.js 的常用命令
- 2. 安装 http-server 服务
- 3. 使用 http-server 开启服务
-
- 1)使用 http-server
- 2)详解 http-server [path] [options]
- 二、Web 静态服务器
-
- 1. 显示固定的页面
-
- 1)Python 代码
- 2)结果展示
- 2. 显示请求的页面
-
- 1)Python 代码
- 2)结果展示
- 3. 多进程显示页面
- 4. 多线程显示页面
- 5. 非阻塞模式显示页面
- 6. 利用 epoll 显示页面(Linux 下运行)
- 7. 利用 gevent 显示页面
有关 HTTP 的基础知识:【应用层 IV(万维网WWW)【★★】】
一、在本地启动 HTTP 服务器
1. Windows 下安装 node.js
1)下载安装包
node.js 下载网址:【node.js 中文网】
-
进入官网,根据需求下载安装包,注意:
-
.msi 是 Windows 系统下的一种安装包文件格式,这种文件类型包含了某个软件或程序的所有安装信息和必要文件,用户只需按照提示进行安装,即可成功将软件或程序部署到 Windows 系统中。
-
.zip 是程序的压缩包,不需要进行安装,解压即可。
-
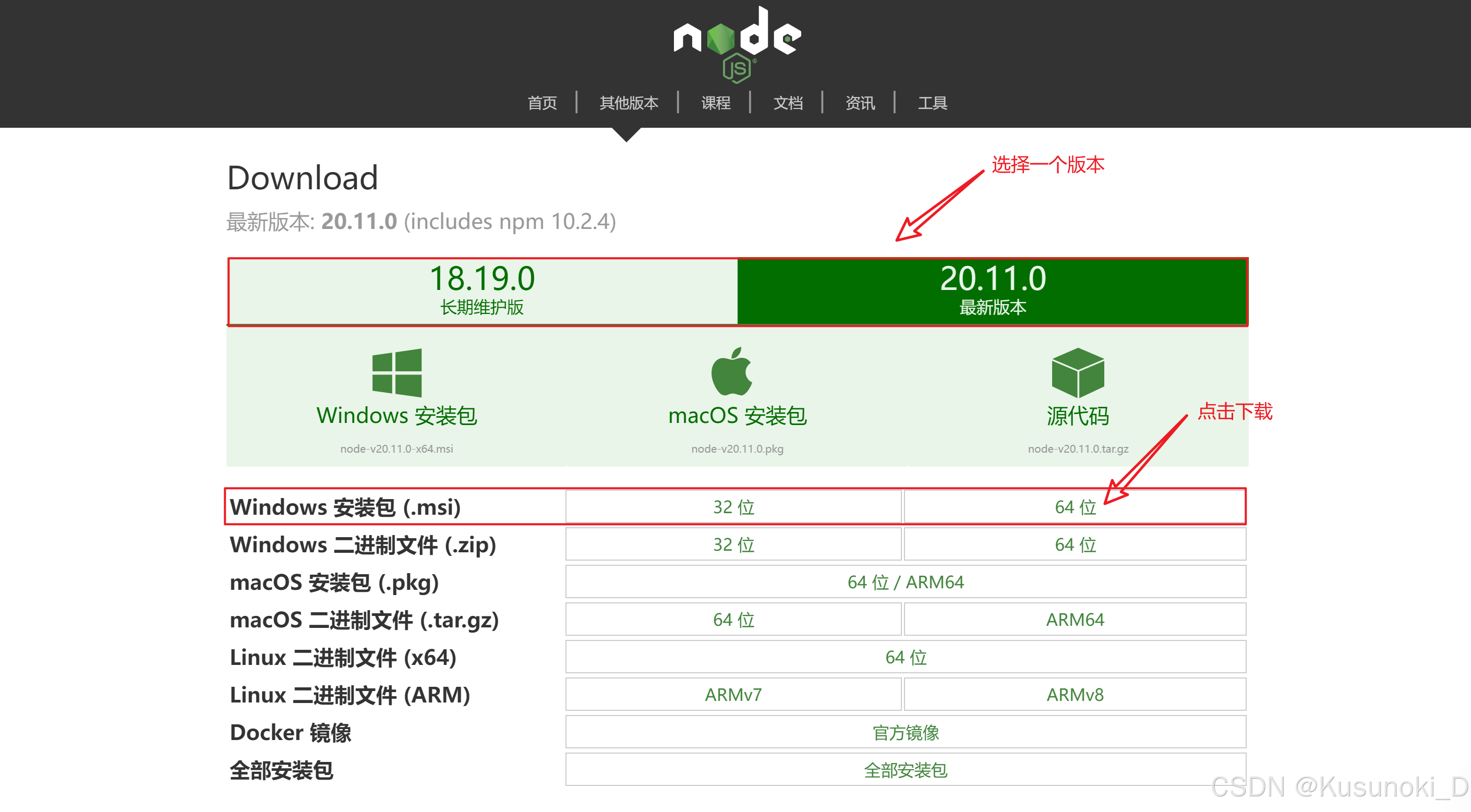
- 根据下图安装软件,可以自行修改安装路径。
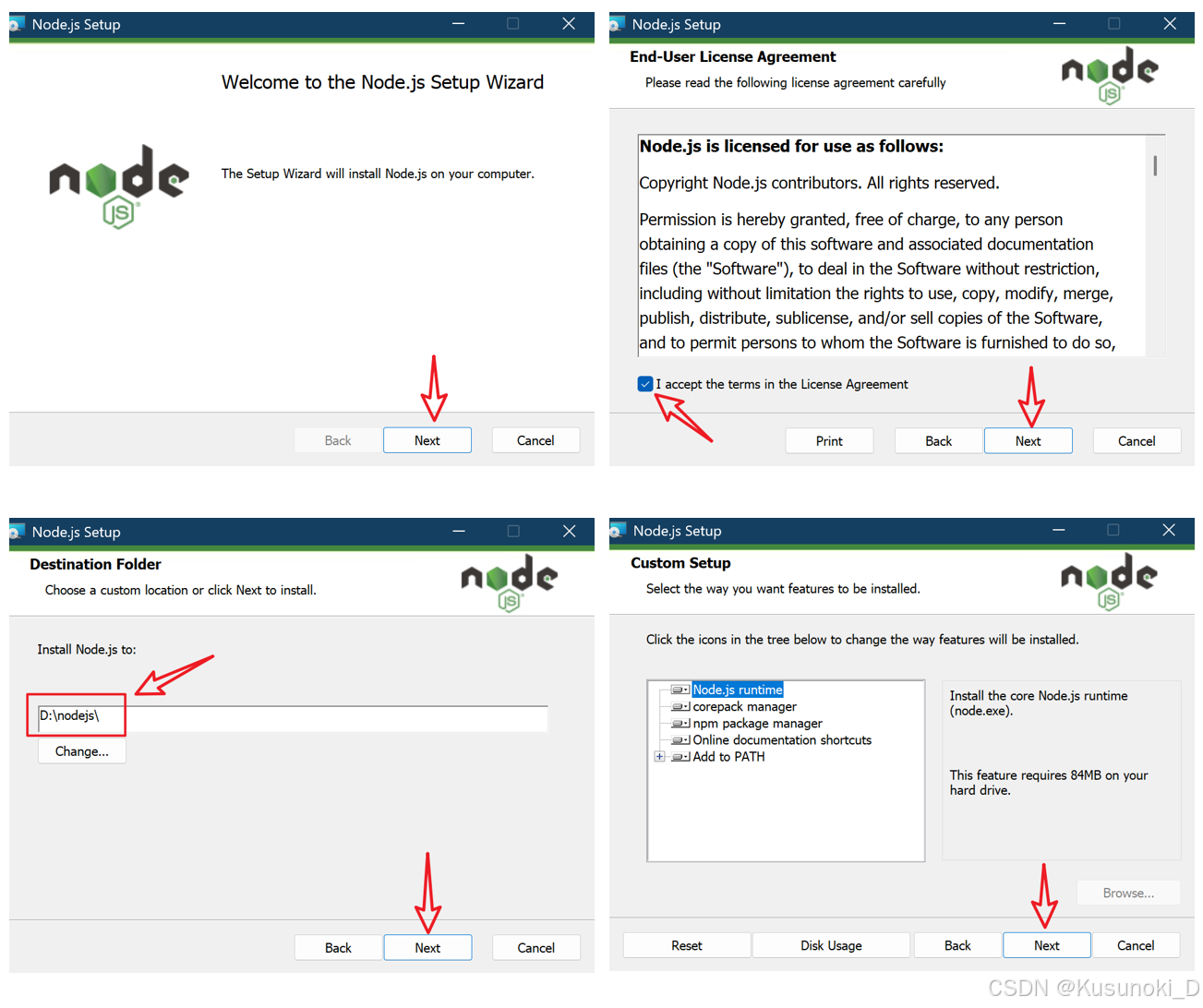
-
安装好后,Win + X 点击 “系统” → “高级系统设置” → “环境变量(N)…” 并双击 “系统变量(S)” 下的 PATH 可以看到新增了一项 D:\\nodejs\\(设置的安装路径)。
-
Win + R 输入 cmd 进入命令提示符,输入 node -v 和 npm -v ,如果输出版本号,则说明 node.js 安装成功。
2)配置环境变量
-
在安装路径 D:\\nodejs\\ 下新建两个文件夹 “node_global” 和 “node_cache” ,并复制它们的路径。
-
以管理员身份运行 cmd ,输入以下两条指令:
npm config set prefix "D:\\nodejs\\node_global"
npm config set cache "D:\\nodejs\\node_cache"
- 可以通过以下两条指令查看配置的路径:
npm config get prefix
npm config get cache
-
Win + X 点击 “系统” → “高级系统设置” → “环境变量(N)…”
-
双击 “用户变量(U)” 下的 PATH ,将 C:\\Users\\[用户名]\\AppData\\Roaming\\npm 修改成 D:\\nodejs\\node_global ;
-
双击 “系统变量(S)” 下的 PATH ,新建 D:\\nodejs\\node_global\\node_modules 和 D:\\nodejs\\node_cache ,最后一路点击确定即可。
注:此时 node_global 文件夹下并无 node_modules 文件夹,没有关系,先进行设置即可。
- 配置完成后,全局安装一个 express 模块进行测试是否配置成功:以管理员身份运行 cmd ,输入指令 npm install express -g ,其中 -g 代表全局安装,此时 node_global 文件夹下才会自动创建一个名为 node_modules 的文件夹。
3)安装镜像
-
以管理员身份运行 cmd ,输入指令 npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com 安装淘宝镜像。
-
输入指令 npm config get registry 查看是否安装成功。
【可选】如果想要使用 cnpm 命令行工具代替默认的 npm ,则进行以下操作:
-
以管理员身份运行 cmd ,输入指令 npm install -g cnpm –registry=https://registry.npmmirror.com 。
-
输入指令 cnpm -v 查看是否安装成功。
4)node.js 的常用命令
- 检查版本
# 检查 Node.js 版本
node -v
# 检查 npm 版本
npm -v
- 初始化项目
# 初始化一个新的 Node.js 项目
npm init
- 安装和卸载包
# 安装特定版本的 Node.js 包
npm install <package-name>@<version>
# 全局安装 Node.js 包
npm install -g <package-name>
# 卸载 Node.js 包
npm uninstall <package-name>
- 查看已安装的包
# 查看全局安装的 Node.js 包
npm list -g –depth 0
# 查看已安装的本地包
npm ls
- 更新包
# 更新所有全局安装的 Node.js 包
npm update -g
# 更新特定 Node.js 包
npm update <package-name>
- 运行代码和启动应用程序
# 运行 Node.js 文件
node <filename.js>
# 使用 nodemon 启动应用程序(自动重启)
nodemon <filename.js>
# 在浏览器中打开应用程序
npm start
# 指定环境变量启动应用程序
NODE_ENV=production node <filename.js>
参考文章: 【node.js安装及环境配置超详细教程【Windows系统安装包方式】】 【2024最新版Node.js下载安装及环境配置教程【保姆级】】 【Node.js安装及环境配置超详细教程【Windows系统】】
2. 安装 http-server 服务
http-server 是一个简单且快速的零配置命令行静态文件服务器,主要用于本地快速启动一个静态文件服务,它通常用于开发和测试环境。
-
以管理员身份运行 cmd ,输入指令 npm install http-server -g 进行全局安装 http-server 服务。
-
输入命令 http-server -v 可查看该服务是否安装成功。
3. 使用 http-server 开启服务
1)使用 http-server
-
Win + R 输入 cmd 进入命令提示符,通过 cd 操作将磁盘路径改至需要开启服务的路径下。
-
输入命令 http-server -p 7890 指定端口开启服务器。
默认的访问地址是:http://127.0.0.1:8080
-
启动成功可以通过 http://127.0.0.1:7890 进行访问。
-
按下 Ctrl + C 终止服务。
2)详解 http-server [path] [options]
以下是 http-server 常用的一些命令和参数:
| [path] | 指定服务器根目录,默认当前目录 | http-server ./public |
| -p or –port <port> | 指定监听端口,默认 8080 | http-server -p 3000 |
| -a or –address <address> | 绑定的地址,默认 0.0.0.0(所有地址) | http-server -a 127.0.0.1 |
| -c or –cache <time> | 缓存时间(秒) | http-server -c 3600 |
| -c-1 | -1 表示禁用缓存 | http-server -c-1 |
| -d or –directory | 启用目录列表显示 | http-server -d |
| -i or –index <file> | 指定默认首页文件 | http-server -i index.html |
| -h or –help | 显示帮助信息 | http-server -h |
| -o or –open | 启动时自动在浏览器打开 | http-server -o |
| -g or –gzip | 启用 gzip 压缩 | http-server -g |
| -e or –ext <extension> | 设置默认扩展名,默认 html | http-server -e htm |
| -s or –silent | 静默模式,不输出任何日志信息 | http-server -s |
| -r or –robots <file> | 指定 robots.txt 文件位置 | http-server -r ./robots.txt |
| –cors | 启用 CORS 跨域 | http-server –cors |
| -S or –ssl | 启用 HTTPS | http-server –ssl –cert ./cert.pem –key ./key.pem |
| -C or –cert <file> | SSL 证书文件路径 | http-server -S -C ./cert.pem -K ./key.pem |
| -K or –key <file> | SSL 私钥文件路径 | http-server -S -C ./cert.pem -K ./key.pem |
| -U or –utf8 | 对 URL 使用 UTF-8 编码 | http-server -U |
| -P or –proxy <url> | 代理未找到的请求到指定 URL | http-server -P http://example.com |
参考文章:【http-server使用,启动本地服务器 & 使用serve包本地启动】
二、Web 静态服务器
1. 显示固定的页面
1)Python 代码
# 服务器端
import socket
def service_client(client_socket):
# 1. 接收浏览器发送过来的请求 ,即 http 请求
recv_data = client_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
request_header_lines = recv_data.splitlines()
for line in request_header_lines:
print(line)
# 2. 返回 http 格式的数据,给浏览器
response_headers = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n" # 200 表示找到这个资源
response_headers += "\\r\\n" # 用一个空的行与 body 进行隔开
response_body = "hello world"
# 将 response header 和 response body 发送给浏览器
response = response_headers + response_body
client_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
client_socket.close()
def main():
# 1. 创建 TCP 套接字
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
# 设置服务器端 4 次挥手之后资源能够立即释放,这样就保证下次运行程序时 可以立即绑定 8888 端口
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号,127.0.0.1 是本机对自己的网络地址,即本地回环地址
ip = "127.0.0.1"
port = 8888
server_socket.bind((ip, port))
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
server_socket.listen(128)
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
client_socket, client_addr = server_socket.accept()
# print(f'—Client [{client_addr[0]}:{client_addr[1]}] Link Success—')
# 5. 为这个客户端服务
service_client(client_socket)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
实现步骤:
2)结果展示
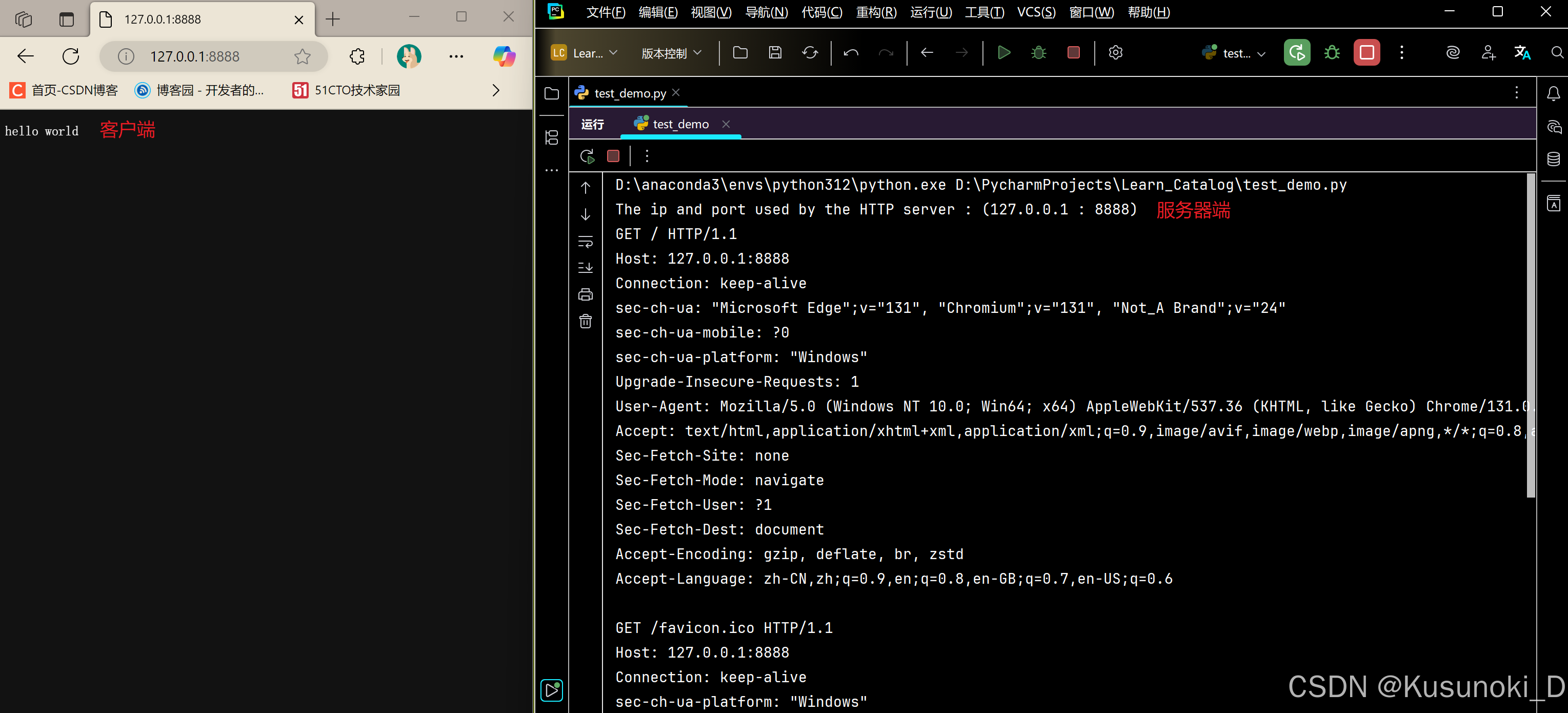
右击浏览器页面,选择 “检查” → “网络” ,输入 Ctrl + R 刷新纪录,再单击想要查看的名称就可以查看详细的标头信息。
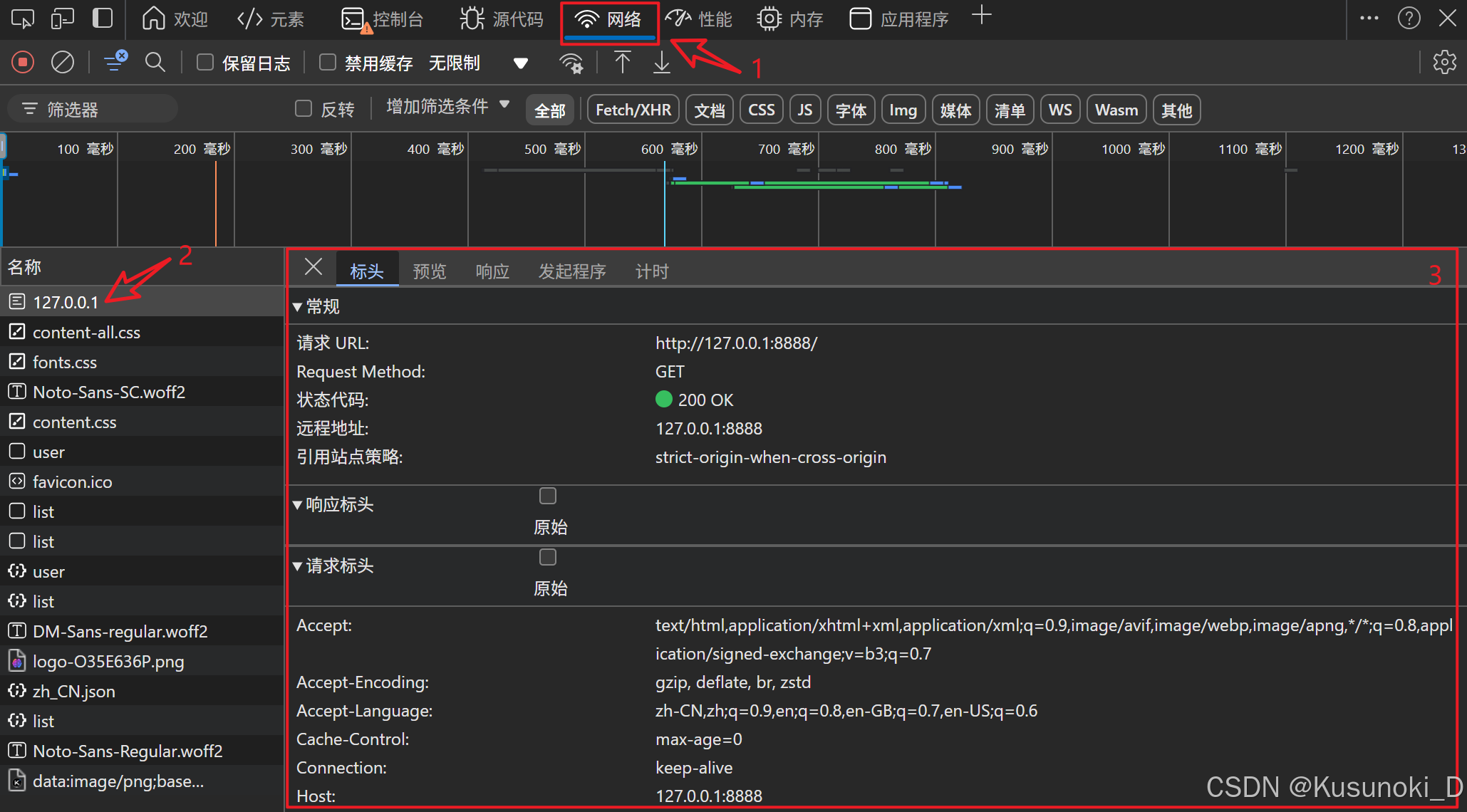
2. 显示请求的页面
1)Python 代码
import socket
import re
import time
# 服务器端
def service_client(new_socket, time_start):
# 1. 接收浏览器发送过来的请求 ,即 http 请求
request = new_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
# 得到头部的每一行
request_lines = request.splitlines()
if request_lines:
# 使用正则表达式获取请求的 url
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
# 例如:'GET /how-to-learn-qt.html HTTP/1.1'
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
# 例如:/how-to-learn-qt.html
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print(">" * 30, file_name) # 输出请求的 url
for request_line in request_lines:
print(request_line) # 输出请求
# 2. 返回 http 格式的数据,给浏览器
try:
f = open("./../html" + file_name, "rb") # 打开请求的资源
# 找不到资源就返回 404 Not Found
except FileNotFoundError:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——File Not Found—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
else:
response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
html_content = f.read() # body
f.close()
new_socket.settimeout(5)
try:
# 2.1 将 response header 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 2.2 将 response body 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(html_content)
# 发送超时
except socket.timeout:
response = "HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Timeout\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——Send Timeout—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 关闭套接字
new_socket.close()
time_end = time.time()
print(f'The total time spent is {time_end – time_start} seconds.')
print('-' * 50)
def main():
# 1. 创建 TCP 套接字
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号
ip = "127.0.0.1"
port = 7890
tcp_server_socket.bind((ip, port))
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
new_socket, client_addr = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# print(f'—Client [{client_addr[0]}:{client_addr[1]}] Link Success—')
time_start = time.time()
# 5. 为这个客户端服务
service_client(new_socket, time_start)
# 关闭监听套接字
# tcp_server_socket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
HTML 资源下载:【Python 实现 Web 静态服务器中需要使用到的 HTML 资源】
实现步骤:
2)结果展示
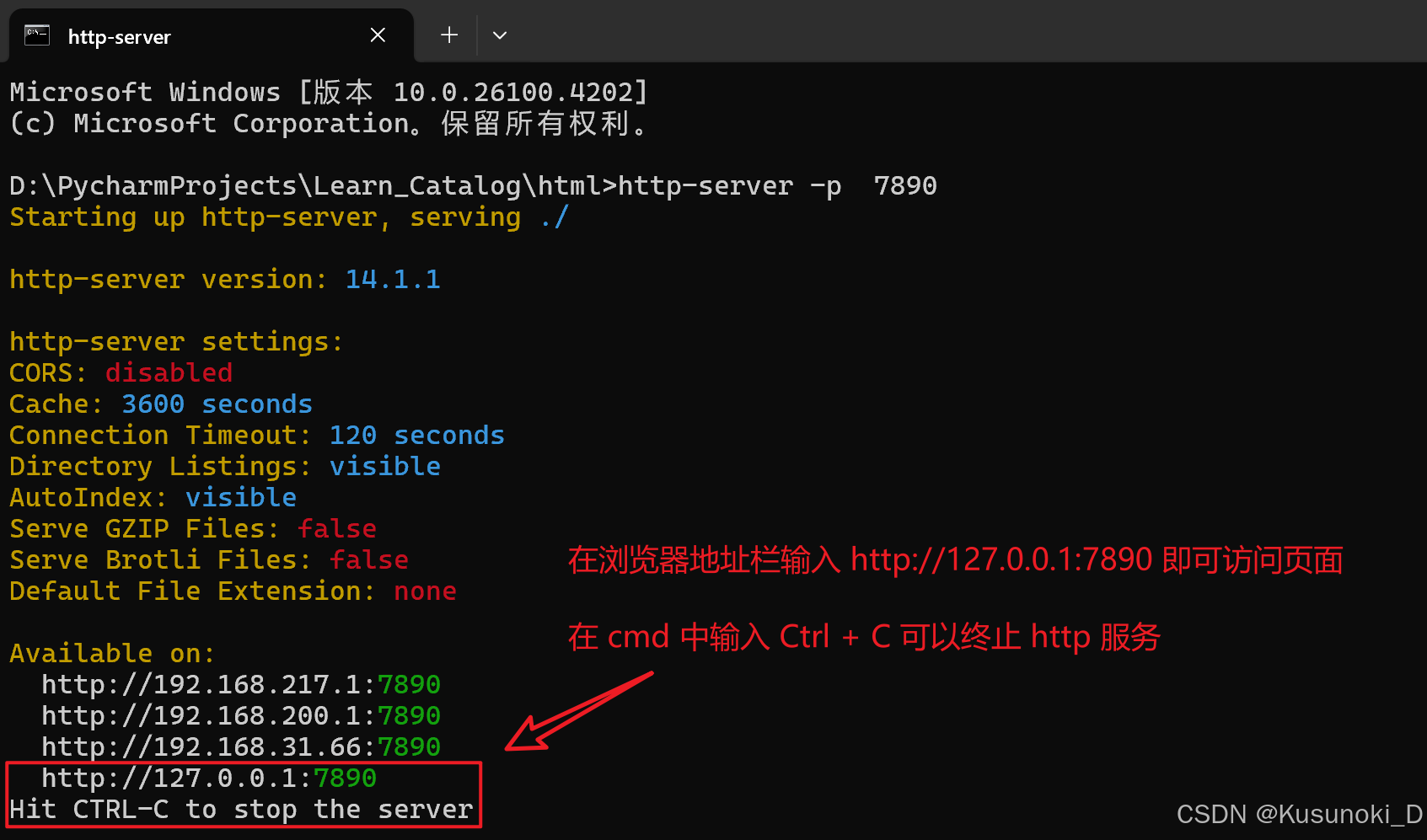

3. 多进程显示页面
Python 代码:
import socket
import re
import multiprocessing
import time
# 服务器端
def service_client(new_socket, time_start):
# 1. 接收浏览器发送过来的请求 ,即 http 请求
request = new_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
# 得到头部的每一行
request_lines = request.splitlines()
if request_lines:
# 使用正则表达式获取请求的 url
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
# 例如:'GET /how-to-learn-qt.html HTTP/1.1'
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
# 例如:/how-to-learn-qt.html
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print(">" * 30, file_name) # 输出请求的 url
for request_line in request_lines:
print(request_line) # 输出请求
# 2. 返回 http 格式的数据,给浏览器
try:
f = open("./../html" + file_name, "rb") # 打开请求的资源
# 找不到资源就返回 404 Not Found
except FileNotFoundError:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——File Not Found—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
else:
response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
html_content = f.read() # body
f.close()
new_socket.settimeout(5)
try:
# 2.1 将 response header 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 2.2 将 response body 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(html_content)
# 发送超时
except socket.timeout:
response = "HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Timeout\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——Send Timeout—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 关闭子进程
new_socket.close()
time_end = time.time()
print(f'The total time spent is {time_end – time_start} seconds.')
print('-' * 50)
def main():
# 1. 创建 TCP 套接字
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号
ip = "127.0.0.1"
port = 7890
tcp_server_socket.bind((ip, port))
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
new_socket, client_addr = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# print(f'—Client [{client_addr[0]}:{client_addr[1]}] Link Success—')
time_start = time.time()
# 5. 为这个客户端服务
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=service_client, args=(new_socket, time_start))
p.start()
# 关闭父进程
new_socket.close()
# 关闭监听套接字
# tcp_server_socket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
实现步骤:
4. 多线程显示页面
Python 代码:
import socket
import re
import threading
import time
# 服务器端
def service_client(new_socket, time_start):
# 1. 接收浏览器发送过来的请求 ,即 http 请求
request = new_socket.recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
# 得到头部的每一行
request_lines = request.splitlines()
if request_lines:
# 使用正则表达式获取请求的 url
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
# 例如:'GET /how-to-learn-qt.html HTTP/1.1'
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
# 例如:/how-to-learn-qt.html
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print(">" * 30, file_name) # 输出请求的 url
for request_line in request_lines:
print(request_line) # 输出请求
# 2. 返回 http 格式的数据,给浏览器
try:
f = open("./../html" + file_name, "rb") # 打开请求的资源
# 找不到资源就返回 404 Not Found
except FileNotFoundError:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——File Not Found—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
else:
response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
html_content = f.read() # body
f.close()
new_socket.settimeout(5)
try:
# 2.1 将 response header 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 2.2 将 response body 发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(html_content)
# 发送超时
except socket.timeout:
response = "HTTP/1.1 504 Gateway Timeout\\r\\n" # header
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——Send Timeout—–" # body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 关闭子线程
new_socket.close()
time_end = time.time()
print(f'The total time spent is {time_end – time_start} seconds.')
print('-' * 50)
def main():
# 1. 创建 TCP 套接字
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号
tcp_server_socket.bind(("127.0.0.1", 7890))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
new_socket, client_addr = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# print(f'—Client [{client_addr[0]}:{client_addr[1]}] Link Success—')
time_start = time.time()
# 5. 为这个客户端服务
p = threading.Thread(target=service_client, args=(new_socket, time_start))
p.start()
# 多线程时,new_socket 传递给子线程以后,主线程不能关闭
# new_socket.close()
# 关闭监听套接字
# tcp_server_socket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
实现步骤:
5. 非阻塞模式显示页面
Python 代码:
import time
import socket
import sys
import re
# 定义一个 WSGI 服务器的类
class WSGIServer(object):
def __init__(self, ip, port, documents_root):
# 1. 创建套接字
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定本地信息
self.server_socket.bind((ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
self.server_socket.listen(128)
# 4. 设置非阻塞
self.server_socket.setblocking(False)
# 客户列表
self.client_socket_list = list()
# 静态资源的路径
self.documents_root = documents_root
def run_forever(self): # 运行服务器
while True:
# 等待对方链接
try:
new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept()
# 未有浏览器链接
except BlockingIOError:
pass
else:
time_start = time.time()
# 设置非阻塞
new_socket.setblocking(False)
# 添加客户至客户列表
self.client_socket_list.append([new_socket, new_addr, time_start])
print(f'New client ({new_addr[0]} : {new_addr[1]}) link success')
# 遍历列表中的连接,如果有浏览器发过来数据,那么就处理
for client_socket in self.client_socket_list:
try:
request = client_socket[0].recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
except BlockingIOError:
pass
else:
if request: # 有数据就处理数据
print(f'Client [{client_socket[1][1]}] is working')
self.deal_with_request(request, client_socket[0])
else: # 客户与浏览器断开
client_socket[0].close()
time_end = time.time()
print(f'Client [{client_socket[1][1]}] finish request')
print(f'The total time spent is {time_end – client_socket[2]} seconds.')
self.client_socket_list.remove(client_socket)
def deal_with_request(self, request, client_socket): # 处理数据
request_lines = request.splitlines()
# 例如:'GET /how-to-learn-qt.html HTTP/1.1'
ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
# 例如:/how-to-learn-qt.html
file_name = ret.group(2)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print(">" * 30, file_name)
for i, line in enumerate(request_lines):
print(i, line)
# 读取文件数据
try:
f = open(self.documents_root + file_name, "rb")
except PermissionError:
response_body = "file not found,Please enter the correct URL"
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\\r\\n"
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\\r\\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\\r\\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\\r\\n"
# 将 header 返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8'))
# 将 body 返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_body.encode("utf-8"))
else:
content = f.read()
f.close()
response_body = content
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\\r\\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\\r\\n"
# 将 header 和 body 返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body)
# 设置服务器服务静态资源时的路径
DOCUMENTS_ROOT = "./../html"
def main(): # 控制 web 服务器整体
if len(sys.argv) == 3:
ip = sys.argv[1]
port = sys.argv[2]
if port.isdigit():
port = int(port)
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
http_server = WSGIServer(ip, port, DOCUMENTS_ROOT)
http_server.run_forever()
else:
print('The port number was entered incorrectly')
else:
print("Run the command : python3 4.non-blocking.py 127.0.0.1 7890")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
实现步骤:
“BlockingIOError: [WinError 10035] 无法立即完成一个非阻止性套接字操作” 的解决方法见:【Python BlockingIOError 阻塞错误】
6. 利用 epoll 显示页面(Linux 下运行)
Python 代码:
# !/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import socket
import select
import re
BASE_PATH = './../html'
# 服务器端
def service_client(new_socket, request):
request_lines = request.splitlines()
if not request_lines:
return
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print("*" * 50, file_name)
print(request)
# 2. 返回 http 格式的数据,给浏览器
try:
f = open(BASE_PATH + file_name, "rb")
except FileNotFoundError:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\\r\\n"
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——file not found—–"
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
else:
html_content = f.read()
f.close()
response_body = html_content
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n"
response_header += "Content-Length:%d\\r\\n" % len(response_body)
response_header += "\\r\\n"
response = response_header.encode("utf-8") + response_body
new_socket.send(response)
def main():
# 1. 创建套接字
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号
ip = "192.168.200.128"
port = 7890
tcp_server_socket.bind((ip, port))
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
# 将套接字变为非堵塞
tcp_server_socket.setblocking(False)
# 4. 创建一个epoll对象
epl = select.epoll()
# 将监听套接字对应的 fd 注册到 epoll 中
# 注册并监控 tcp_server_socket, select.EPOLLIN 为可读事件
epl.register(tcp_server_socket.fileno(), select.EPOLLIN)
fd_event_dict = dict()
while True:
# 默认会堵塞,直到 os 监测到数据到来 通过事件通知方式告诉这个程序,此时才会解堵塞
# 轮询注册的事件
fd_event_list = epl.poll()
# [(fd, event), (套接字对应的文件描述符, 这个文件描述符到底是什么事件)]
for fd, event in fd_event_list:
# 等待新客户端的链接
if fd == tcp_server_socket.fileno():
new_socket, client_addr = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# 注册并监控 new_socket
epl.register(new_socket.fileno(), select.EPOLLIN)
fd_event_dict[new_socket.fileno()] = new_socket
# 判断已经链接的客户端是否有数据发送过来
elif event == select.EPOLLIN:
recv_data = fd_event_dict[fd].recv(4096).decode("utf-8")
# 有数据则处理数据,通过不遍历来定位 socket
if recv_data:
service_client(fd_event_dict[fd], recv_data)
# 客户与浏览器断开
else:
fd_event_dict[fd].close()
# 取消注册
epl.unregister(fd)
# 从字典中移除
del fd_event_dict[fd]
# 关闭监听套接字
# tcp_server_socket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
实现步骤:
配置 PyCharm 连接远程服务器的步骤见:【Python-简单网络编程 I】
7. 利用 gevent 显示页面
Python 代码:
import gevent
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
import socket
import re
BASE_PATH = './../html'
def service_client(new_socket):
# 接收 http 请求
request = new_socket.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
if request:
request_lines = request.splitlines()
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
print(">" * 30, file_name)
print(request) # 输出请求
try:
f = open(BASE_PATH + file_name, "rb")
except FileNotFoundError:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\\r\\n"
response += "\\r\\n"
response += "——-file not found——-"
new_socket.send(response)
else:
html_content = f.read()
f.close()
response = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\\r\\n"
response += "\\r\\n"
new_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8'))
new_socket.send(html_content)
new_socket.close()
def main():
# 1. 初始化
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 确保端口复用
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定 IP 和端口号
ip = "127.0.0.1"
port = 7890
tcp_server_socket.bind((ip, port))
print("The ip and port used by the HTTP server : (%s : %s)" % (ip, port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
new_socket, socket_addr = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# print(f'New client ({socket_addr[0]} : {socket_addr[1]}) link success')
# 创建一个普通的 greenlet 对象并切换
gevent.spawn(service_client, new_socket)
# tcp_server_socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
实现步骤:
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心


评论前必须登录!
注册