1.基本原理
(1) 初始化:设定初始解(待优化变量的初始值)、初始高温(如 100)、温度衰减率(如 0.99)、终止温度(如 1e-8),计算初始解的目标函数值(“能量”),并记录为当前最优解。
(2)迭代降温:在当前温度下,对当前解做随机扰动生成新解,计算新解的能量,得到能量差值(新解 – 当前解)。
(3)Metropolis 准则(接受新解):若新解更优(能量更小):直接接受新解,更新当前解;
若新解更差:以概率 e =exp(−ΔE/T) 接受(T 为当前温度,ΔE 为能量差),温度越高,接受差解的概率越大。
(4)更新最优解:若当前解优于历史最优解,更新全局最优解。
(5)降温与终止:按衰减率降低温度,重复(2)、(3)、(4),直到满足终止条件(如收敛、将至最低温度)停止迭代,输出最优解。
2.代码实现
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"使用设备: {device}")
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print(f"GPU名称: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}")
# ————————– 2. 定义目标函数(GPU张量版) ————————–
def target_function(x):
return x ** 2 + 10 * torch.sin(x) + 5 * torch.cos(3 * x)
def simulated_annealing_gpu(func, # 目标函数
init_x, # 初始解(GPU张量)
init_temp=100, # 初始温度
min_temp=1e-8, # 终止温度
decay_rate=0.99, # 温度衰减率
step_size=0.5 # 新解生成的步长
):
current_x = init_x.to(device)
best_x = current_x.clone()
current_energy = func(current_x)
best_energy = current_energy.clone()
temp = torch.tensor(init_temp, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
# 迭代降温
iteration = 0
while temp > min_temp:
iteration += 1
new_x = current_x + step_size * torch.randn_like(current_x, device=device)
new_energy = func(new_x)
energy_diff = new_energy – current_energy
if energy_diff < 0:
accept = True
else:
accept_prob = torch.exp(-energy_diff / temp)
accept = torch.rand(1, device=device) < accept_prob
if accept:
current_x = new_x
current_energy = new_energy
if current_energy < best_energy:
best_x = current_x.clone()
best_energy = current_energy.clone()
temp *= decay_rate
if iteration % 100 == 0:
print(f"迭代次数: {iteration}, 当前温度: {temp.item():.6f}, 最优值: {best_energy.item():.4f}")
return best_x, best_energy
if __name__ == "__main__":
init_x = torch.tensor(2.0, device=device) # 初始值设为2.0
best_x, best_energy = simulated_annealing_gpu(
func=target_function,
init_x=init_x,
init_temp=100,
min_temp=1e-8,
decay_rate=0.99,
step_size=0.5
)
best_x_cpu = best_x.cpu().item()
best_energy_cpu = best_energy.cpu().item()
print("\\n===== 优化结果 =====")
print(f"最优解 x: {best_x_cpu:.4f}")
print(f"最优目标函数值: {best_energy_cpu:.4f}")
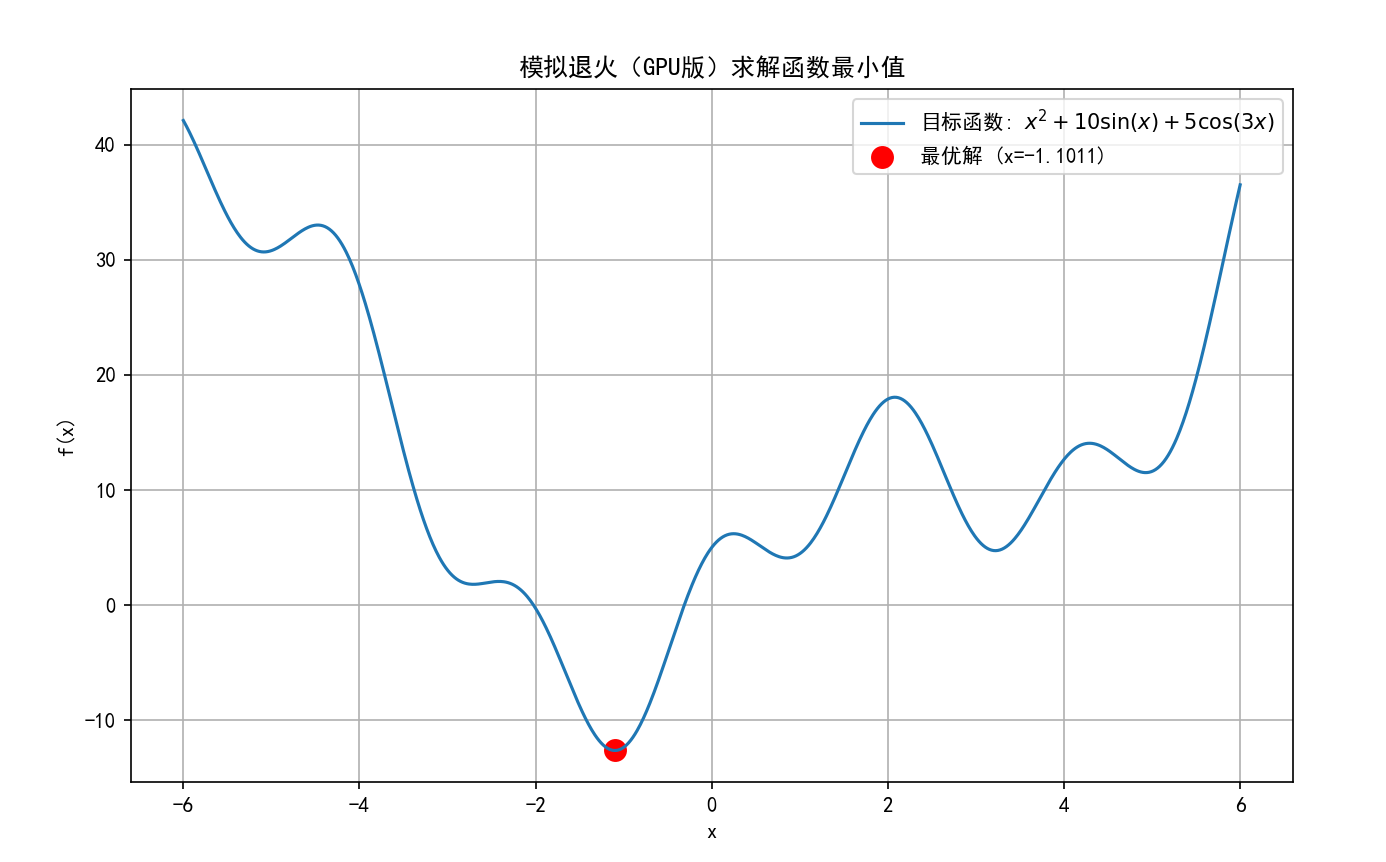
# ————————– 可视化验证 ————————–
x_range = np.linspace(-6, 6, 1000)
y_range = target_function(torch.tensor(x_range, device=device)).cpu().numpy()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x_range, y_range, label="目标函数: $x^2 + 10\\sin(x) + 5\\cos(3x)$")
plt.scatter(best_x_cpu, best_energy_cpu, color="red", s=100, label=f"最优解 (x={best_x_cpu:.4f})")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("f(x)")
plt.title("模拟退火(GPU版)求解函数最小值")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
运行效果:
使用设备: cpu
迭代次数: 100, 当前温度: 36.603275, 最优值: 4.1254
迭代次数: 200, 当前温度: 13.397995, 最优值: -12.6188
迭代次数: 300, 当前温度: 4.904105, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 400, 当前温度: 1.795063, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 500, 当前温度: 0.657052, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 600, 当前温度: 0.240502, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 700, 当前温度: 0.088032, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 800, 当前温度: 0.032222, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 900, 当前温度: 0.011794, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1000, 当前温度: 0.004317, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1100, 当前温度: 0.001580, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1200, 当前温度: 0.000578, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1300, 当前温度: 0.000212, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1400, 当前温度: 0.000077, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1500, 当前温度: 0.000028, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1600, 当前温度: 0.000010, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1700, 当前温度: 0.000004, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1800, 当前温度: 0.000001, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 1900, 当前温度: 0.000001, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 2000, 当前温度: 0.000000, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 2100, 当前温度: 0.000000, 最优值: -12.6395
迭代次数: 2200, 当前温度: 0.000000, 最优值: -12.6395
===== 优化结果 =====
最优解 x: -1.0995
最优目标函数值: -12.6395
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心



评论前必须登录!
注册