对于STM32F103C8T6集成版进行小升级,加入了光敏电阻,热敏电阻,8个小灯,两个按键,macial口改成了type-c,然后改成了自动下载
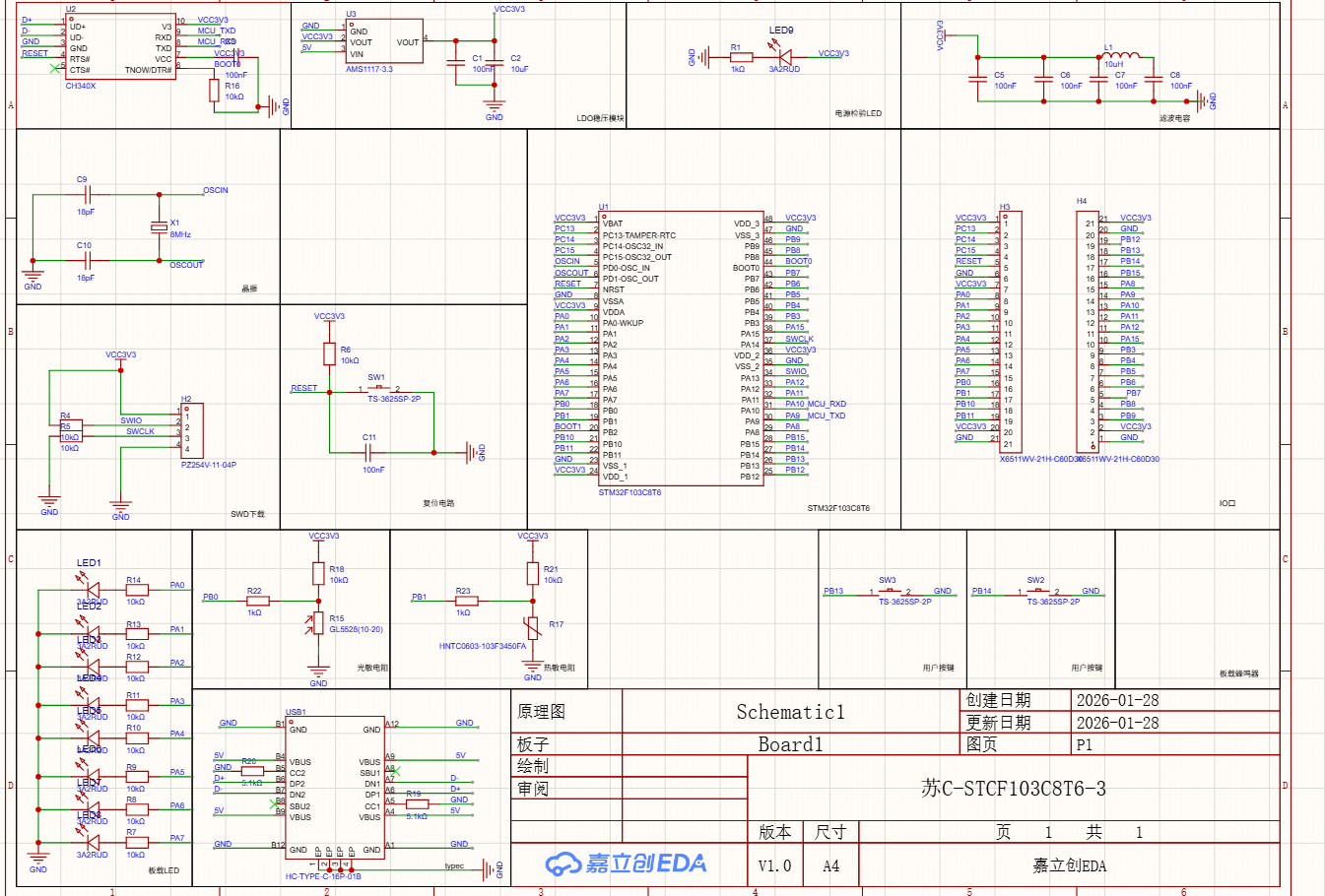
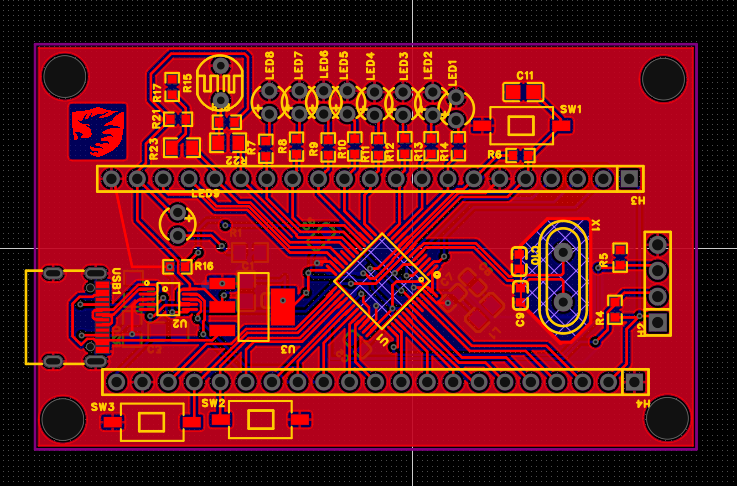
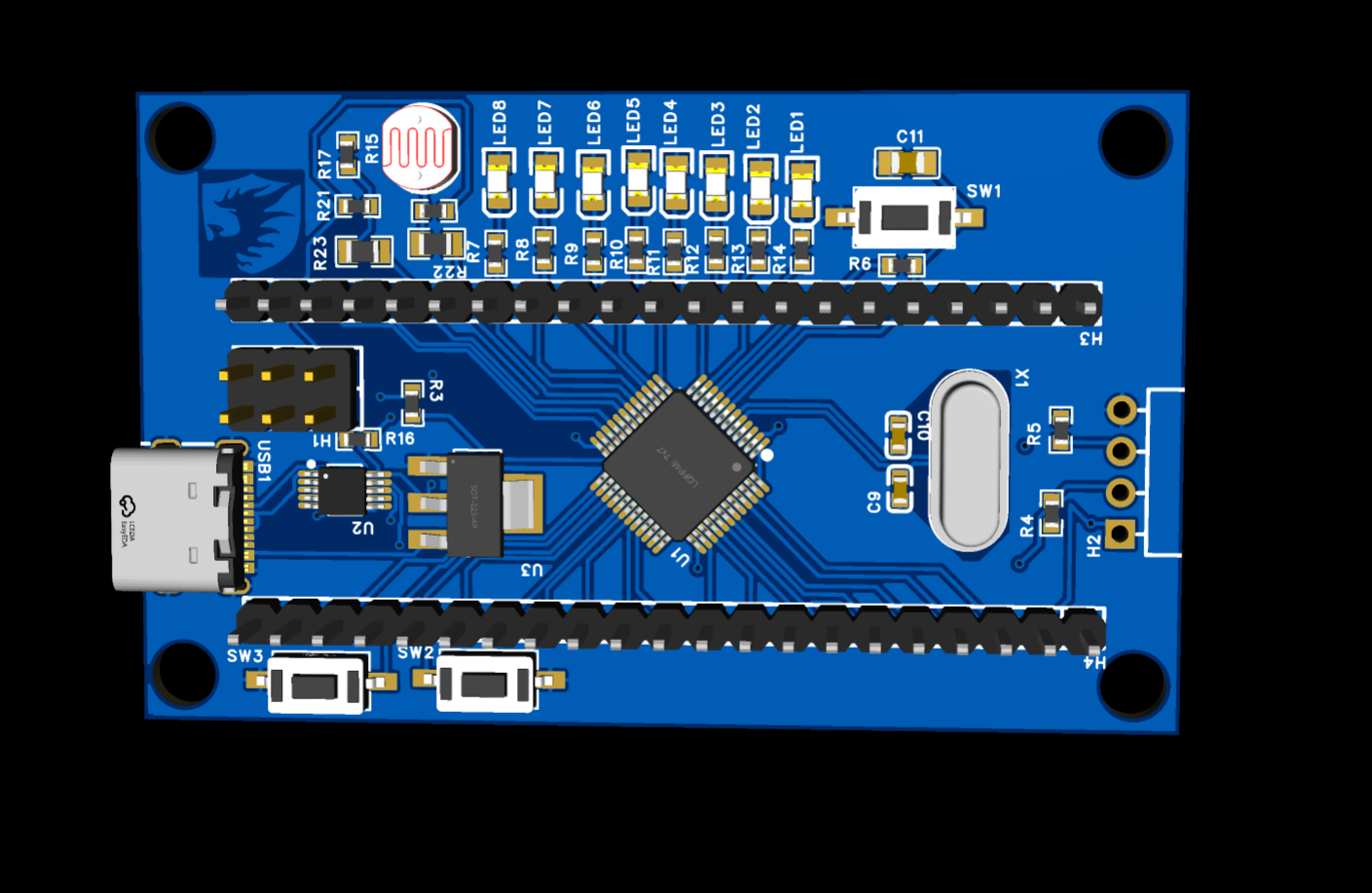
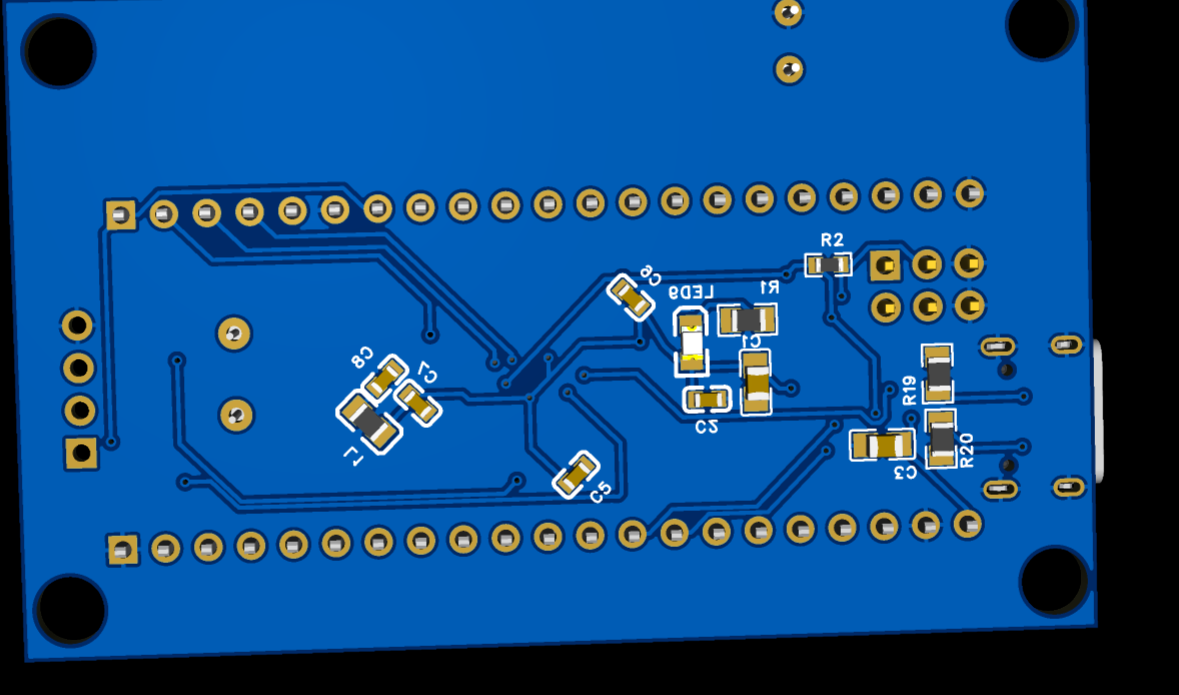
然后为了省钱又全部改成直插式的了
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义结构体数据类型
typedef struct Student
{
int id;
char gender;
char name[20];
char *adress;//未分配内存空间之前,是野指针
}student;
void deepcopy(student *to_stu, student *from_stu)
{
to_stu->id = from_stu->id;
to_stu->gender = from_stu->gender;
//错的
//to_stu->name = from_stu->name;
strcpy(to_stu->name,from_stu->name);
to_stu->adress = (char *)malloc(100);
memset(to_stu->adress, 0, sizeof(to_stu->adress));
memcpy(to_stu->adress, from_stu->adress, strlen(from_stu->adress));
}
int main()
{
//定义结构体数据变量
// struct Student stu1 = {.id = 1, .gender = 'M', .name = "Lisi"};
// student stu2 = {2, 'F', "xiaohong"};
// student *stu = &stu2;
// printf("stu1.id = %d, stu1.gender = %c, stu1.name = %s\\n", (&stu1)->id, stu1.gender, stu1.name);
// printf("stu2.id = %d, stu2.gender = %c, stu2.name = %s\\n", (*stu).id, stu->gender, stu->name);
struct Student stu1 = {1, 'M'};
// printf("please input your message:\\n");
// scanf("%d %c",&stu1.id, &stu1.gender);
printf("please input your address:\\n");
stu1.adress = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);
scanf("%s",stu1.adress);
//结构体成员是数组的不能用“=”来赋值
//stu1.name = "lisi";
strcpy(stu1.name, "lisi");
printf("stu1.id = %d, stu1.gender = %c, stu1.name = %s\\n", (&stu1)->id, stu1.gender, stu1.name);
printf("address:%s\\n",stu1.adress);
//结构体变量之间的赋值,浅拷贝问题
student stu2; //= stu1;
deepcopy(&stu2, &stu1);
free(stu1.adress);
stu1.adress = NULL;
printf("stu2.id = %d, stu2.gender = %c, stu2.name = %s\\n", stu2.id, stu2.gender, stu2.name);
printf("address:%s\\n",stu2.adress);
free(stu2.adress);
stu2.adress = NULL;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct Student
{
int id;
char gender;
char name[20];
};
//结构体字节对齐是什么
//结构体的内存对齐
//要在最大的数据类型上根据你代码中的注释,我来详细讲解结构体对齐规则:
// 结构体对齐规则
// 核心规则:
// 对齐值:结构体中最大成员的类型大小(如int为4,double为8)
// 成员偏移:每个成员的偏移量必须是其类型大小的整数倍
// 结构体总大小:必须是最大成员大小的整数倍
// 以你的struct Student为例:
// struct Student {
// int id; // 4字节,偏移0 ✓
// char gender; // 1字节,偏移4 ✓
// char name[20]; // 20字节,偏移5 (5%4=1,不满足)
// };
// 问题:name偏移量为5,但应该是4的倍数(因为最大成员是int,4字节)
// 内存布局:
// 偏移 0-3: id (4字节)
// 偏移 4: gender (1字节)
// 偏移 5: 填充3字节 (对齐到偏移8)
// 偏移 8-27: name (20字节)
// 总大小:28字节
// 实际输出:28
// 优化版本(按类型大小从大到小排列):
// struct Student {
// int id; // 偏移0,4字节
// char name[20]; // 偏移4,20字节
// char gender; // 偏移24,1字节
// char padding[3]; // 填充3字节,总大小28字节
// };
// 注意:这个例子中两种写法大小相同,但通常按大小排列能减少浪费。
int main()
{
printf("%d\\n",sizeof(struct Student));
return 0;
}
、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
//共用体union
union Data {
int i;
float f;
char str[20];
} data;
//共用体的特点:所有成员共享同一块内存空间,只能同时存储一个成员的数据
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//关键字volatile的作用
//1.防止编译器优化
//2.防止编译器将变量保存到寄存器中
volatile int i = 0 ;
int *p = &i;
//取地址为什么会报错:
//int *p = &i;
//不能去取i的地址,因为i是volatile的,编译器会认为i的值随时可能发生变化,所以编译器会禁止对i的取地址操作
while(1)
{
printf("i = %d\\n",i);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
void func(void)
{
static int i = 0;
i++;
printf("i = %d\\n",i);
}
int main()
{
//关键字static的作用
//1.修饰局部变量:静态局部变量,生命周期长,作用域局部
//2.修饰全局变量:静态全局变量,生命周期长,作用域全局
//3.修饰函数:静态函数,只能在定义它的文件中使用
//4.修饰类:静态类,只能在定义它的文件中使用
func();
func();
func();
return 0;
}
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心




评论前必须登录!
注册