目录
前言
一、PG数据库设计与实现
1、PG数据库模型设计
2、存储天气物理表结构
二、MybatisPlus中实体实现
1、MybatisPlus实体类图设计
2、MybatisPlus中相关类实现
三、PostgreSQL持久化实现
1、天气数据入库时序图
2、调用程序执行
3、数据入库结果
四、总结
前言
在当今数字化时代,数据的获取、存储与分析已成为推动众多领域发展的重要驱动力。天气数据作为一种极具价值的公共资源,广泛应用于农业、交通、旅游、能源等诸多行业。百度天气作为国内知名的天气信息服务平台,提供了丰富且实时的天气数据,若能将其有效存储并加以利用,将为相关业务决策、研究分析等提供有力支持。将百度天气数据存储至 PostgreSQL 数据库,这一过程涉及数据的获取、解析、转换以及最终的存储等多个环节。通过 MybatisPlus 框架来实现这一目标,不仅可以充分利用其强大的 ORM(对象关系映射)能力,将天气数据的实体类与数据库表结构进行高效映射,还能借助其提供的便捷操作接口,轻松完成数据的增删改查等操作。此外,MybatisPlus 的分页插件、缓存机制等特性,也能够在处理大量天气数据时,有效提升系统的性能和响应速度,确保数据存储过程的高效与稳定。
这一实践过程不仅涉及到技术层面的多种知识融合,如网络编程、JSON 数据处理、数据库操作以及框架应用等,还面临着诸如数据准确性、存储效率、系统稳定性等诸多挑战。通过对整个流程的深入研究和实践探索,我们希望能够为开发者提供一套完整、高效且可靠的解决方案,助力大家更好地利用百度天气数据,挖掘其潜在价值,同时也为类似的数据存储项目提供有益的参考和借鉴。力求以清晰、易懂的方式,带领读者逐步深入这一实践过程,共同探索数据存储与应用的无限可能。本文重点在于详细得介绍在MybatisPlus框架中如何将百度天气信息持久化到PG数据库中,首先介绍具体的PG数据库的设计与实现,然后详细介绍MybatisPlus的实体设计,最后以源代码的形式介绍如何将数据进行持久化,期待为大家提供一种良好的解决方案和参考。
一、PG数据库设计与实现
PostgreSQL 作为一种功能强大的开源关系型数据库管理系统,以其出色的性能、高度的可扩展性以及对复杂数据类型的良好支持,受到越来越多开发者的青睐。它能够高效地存储和管理大规模数据,为数据的查询、分析与挖掘提供了坚实基础。本节首先将以存储百度天气数据为背景,介绍如何进行数据库的物理表设计,为了方便大家学习,这里可以分享相关的建表语句。
1、PG数据库模型设计
在前一篇的内容中,我们详细的介绍了如何将百度天气的返回数据转换为JavaBean,GSON 框架下百度天气 JSON 数据转 JavaBean 的实战攻略。在实际应用系统查询过程中,我们除了要定义JavaBean,也需要定义用来保存天气数据的数据库模型。根据接口文档,我们可以按照业务维度设计以下数据库模型,分别用来存储天气接口返回的数据:
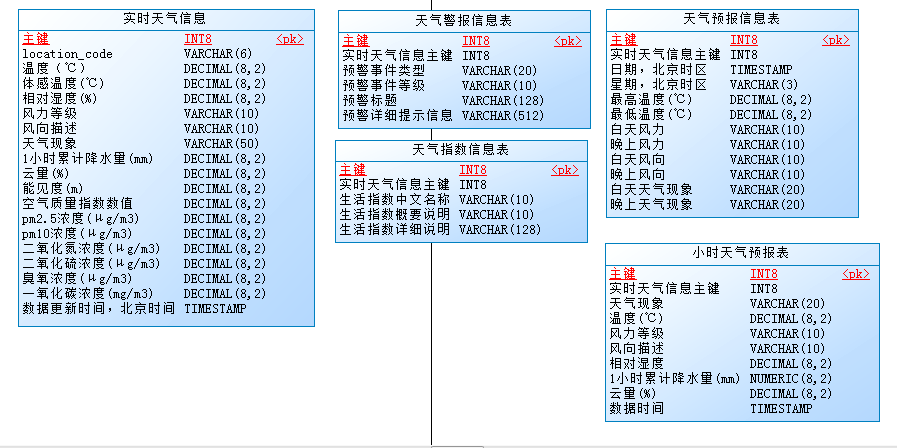
2、存储天气物理表结构
这里将根据上面的物理模型创建相应的天气信息表,这里将分别给出这五张表的物理结构语句。存储实时天气信息:
create table biz_weather_now (
pk_id INT8 not null,
location_code VARCHAR(6) not null default '',
temp DECIMAL(8,2) not null default 999999,
feels_like DECIMAL(8,2) not null default 999999,
rh DECIMAL(8,2) not null default 999999,
wind_class VARCHAR(10) null,
wind_dir VARCHAR(10) null,
text VARCHAR(50) null,
prec_1h DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
clouds DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
vis DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
aqi DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
pm25 DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
pm10 DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
no2 DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
so2 DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
o3 DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
co DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
uptime TIMESTAMP null,
constraint PK_BIZ_WEATHER_NOW primary key (pk_id)
);
comment on table biz_weather_now is
'存储实时天气信息';
comment on column biz_weather_now.pk_id is
'主键';
comment on column biz_weather_now.location_code is
'行政区划code';
comment on column biz_weather_now.temp is
'温度(℃)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.feels_like is
'体感温度(℃)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.rh is
'相对湿度(%)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.wind_class is
'风力等级';
comment on column biz_weather_now.wind_dir is
'风向描述';
comment on column biz_weather_now.text is
'天气现象';
comment on column biz_weather_now.prec_1h is
'1小时累计降水量(mm)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.clouds is
'云量(%)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.vis is
'能见度(m)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.aqi is
'空气质量指数数值';
comment on column biz_weather_now.pm25 is
'pm2.5浓度(μg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.pm10 is
'pm10浓度(μg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.no2 is
'二氧化氮浓度(μg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.so2 is
'二氧化硫浓度(μg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.o3 is
'臭氧浓度(μg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.co is
'一氧化碳浓度(mg/m3)';
comment on column biz_weather_now.uptime is
'数据更新时间,北京时间';
这里需要注意的是,在保存相应的如气温或者指数时,采用的数据库类型不是Int,这也是为了兼容可能的出现浮点数的情况,而小数位,这里初步设计成2位,大家可以根据实际需求进行调整。
天气警报信息表:
create table biz_weather_alerts (
pk_id INT8 not null,
weather_pk_id INT8 null,
type VARCHAR(20) null,
level VARCHAR(10) null,
title VARCHAR(128) null,
desc_info VARCHAR(512) null,
constraint PK_BIZ_WEATHER_ALERTS primary key (pk_id)
);
comment on table biz_weather_alerts is
'天气警报信息表';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.pk_id is
'主键';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.weather_pk_id is
'实时天气信息主键';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.type is
'预警事件类型,参考 天气取值对照表中的预警类型';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.level is
'预警事件等级';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.title is
'预警标题';
comment on column biz_weather_alerts.desc_info is
'预警详细提示信息';
需要注意的是,在警报信息中,desc字段由于是数据库的关键字,在原始接口中返回的desc我们需要变成desc_info字段,天气指数信息表:
create table biz_weather_indexes (
pk_id INT8 not null,
weather_pk_id INT8 null,
name VARCHAR(10) null,
brief VARCHAR(10) null,
detail VARCHAR(128) null,
constraint PK_BIZ_WEATHER_INDEXES primary key (pk_id)
);
comment on column biz_weather_indexes.pk_id is
'主键';
comment on column biz_weather_indexes.weather_pk_id is
'实时天气信息主键';
comment on column biz_weather_indexes.name is
'生活指数中文名称';
comment on column biz_weather_indexes.brief is
'生活指数概要说明';
comment on column biz_weather_indexes.detail is
'生活指数详细说明';
天气预报信息表:
create table biz_weather_forecasts (
pk_id INT8 not null,
weather_pk_id INT8 null,
date TIMESTAMP null,
week VARCHAR(3) null,
high DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
low DECIMAL(8,2) null default 999999,
wc_day VARCHAR(10) null,
wc_night VARCHAR(10) null,
wd_day VARCHAR(10) null,
wd_night VARCHAR(10) null,
text_day VARCHAR(20) null,
text_night VARCHAR(20) null,
constraint PK_BIZ_WEATHER_FORECASTS primary key (pk_id)
);
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.pk_id is
'主键';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.weather_pk_id is
'实时天气信息主键';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.date is
'日期,北京时区';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.week is
'星期,北京时区';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.high is
'最高温度(℃)';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.low is
'最低温度(℃)';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.wc_day is
'白天风力';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.wc_night is
'晚上风力';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.wd_day is
'白天风向';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.wd_night is
'晚上风向';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.text_day is
'白天天气现象,参考天气取值对照表';
comment on column biz_weather_forecasts.text_night is
'晚上天气现象';
小时天气预报表:
create table biz_weather_forecast_hours (
pk_id INT8 not null,
weather_pk_id INT8 null,
text VARCHAR(20) null,
temp_fc DECIMAL(8,2) null,
wind_class VARCHAR(10) null,
wind_dir VARCHAR(10) null,
rh DECIMAL(8,2) null,
prec_1h NUMERIC(8,2) null,
clouds DECIMAL(8,2) null,
data_time TIMESTAMP null,
constraint PK_BIZ_WEATHER_FORECAST_HOURS primary key (pk_id)
);
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.pk_id is
'主键';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.weather_pk_id is
'实时天气信息主键';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.text is
'天气现象';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.temp_fc is
'温度(℃)';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.wind_class is
'风力等级';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.wind_dir is
'风向描述';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.rh is
'相对湿度';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.prec_1h is
'1小时累计降水量(mm)';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.clouds is
'云量(%)';
comment on column biz_weather_forecast_hours.data_time is
'数据时间';
二、MybatisPlus中实体实现
MybatisPlus 则是基于 Mybatis 的增强版本,它不仅继承了 Mybatis 的灵活性和易用性,还通过一系列插件和扩展功能,极大地简化了数据库操作流程,提高了开发效率,尤其在处理复杂业务逻辑和数据持久化方面表现出色。在之前的博客中已经介绍了相关类的设计,下面将结合MybatisPlus来深入讲解这些实体的设计,分别从类图和具体实现两个方面展开。
1、MybatisPlus实体类图设计

通过分析原来的接口以及梳理对象的关系,可以整理出相关的数据关系,比如实时天气信息与预警信息、生活指数信息、逐日预报信息和逐小时预报信息均是一对多的情况。
2、MybatisPlus中相关类实现
由于篇幅有限,这里将前面的内容中剩下的几个JavaBean的代码给出,在之前的内容中已经对BdWeatherDTO.java、WeatherInfoDTO.java、WeatherIndexes.java进行了说明。预警信息JavaBean如下:
package com.yelang.project.weather.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@TableName(value = "biz_weather_alerts")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class WeatherAlerts implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 9180445236146165608L;
@TableId(value ="pk_id")
private Long pkId ;//主键
@TableField(value="weather_pk_id")
private Long weatherPkId;//实时天气信息主键
private String type;//预警事件类型,参考 天气取值对照表中的预警类型
private String level;//预警事件等级
private String title;//预警标题
@TableField(value="desc_info")
@SerializedName("desc")
private String descInfo;//预警详细提示信息
}
逐日天气预报JavaBean代码如下:
package com.yelang.project.weather.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@TableName(value = "biz_weather_forecasts")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class WeatherForecasts implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4929733391294381721L;
@TableId(value ="pk_id")
private Long pkId ;//主键
@TableField(value="weather_pk_id")
private Long weatherPkId;//实时天气信息主键
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date date;//日期,北京时区
private String week;//星期,北京时区
private BigDecimal high = new BigDecimal(999999);//最高温度(℃)
private BigDecimal low = new BigDecimal(999999);//最低温度(℃)
@TableField(value="wc_day")
@SerializedName("wc_day")
private String wcDay;//白天风力
@TableField(value="wc_night")
@SerializedName("wc_night")
private String wcNight;//晚上风力
@TableField(value="wd_day")
@SerializedName("wd_day")
private String wdDay;//白天风向
@TableField(value="wd_night")
@SerializedName("wd_night")
private String wdNight;//晚上风向
@TableField(value="text_day")
@SerializedName("text_day")
private String textDay;//白天天气现象,参考天气取值对照表
@TableField(value="text_night")
@SerializedName("text_night")
private String textNight;//晚上天气现象
}
最后还有逐小时的天气预报信息JavaBean:
package com.yelang.project.weather.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@TableName(value = "biz_weather_forecast_hours")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class WeatherForecastHours implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -18102820381727782L;
@TableId(value ="pk_id")
private Long pkId ;//主键
@TableField(value="weather_pk_id")
private Long weatherPkId;//实时天气信息主键
private String text;//天气现象
@TableField(value="temp_fc")
@SerializedName("temp_fc")
private BigDecimal tempFc;//温度(℃)
@TableField(value="wind_class")
@SerializedName("wind_class")
private String windClass;//风力等级
@TableField(value="wind_dir")
@SerializedName("wind_dir")
private String windDir;//风向描述
private BigDecimal rh;//相对湿度
@TableField(value="prec_1h")
@SerializedName("prec_1h")
private BigDecimal prec1h;//1小时累计降水量(mm)
private BigDecimal clouds;//云量(%)
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@TableField(value="data_time")
@SerializedName("data_time")
private Date dataTime;//数据时间
}
经过以上的步骤,我们就完成了全部的百度天气相关的JavaBean的定义,接下来我们将详细介绍如何实现将数据持久化到PG数据库中。
三、PostgreSQL持久化实现
在实际开发过程中,我们首先需要通过百度天气 API 获取原始的天气数据,这些数据通常以 JSON 格式返回,包含了城市、日期、温度、湿度、风力、天气状况等诸多信息。随后,利用 Java 等编程语言对这些 JSON 数据进行解析,将其转换为符合数据库存储要求的结构化数据。接着,借助 MybatisPlus 框架,将这些结构化数据映射到对应的实体类中,并通过配置 MybatisPlus 的 SQL 会话工厂、数据源以及相关映射文件,实现与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接和数据的持久化存储。关于如何采集数据、JSON数据转换的内容在之前的博客中都有所涉及,接下来我们来讲解最后一个环节,即如何将采集和转换后的数据持久到PG数据库中。
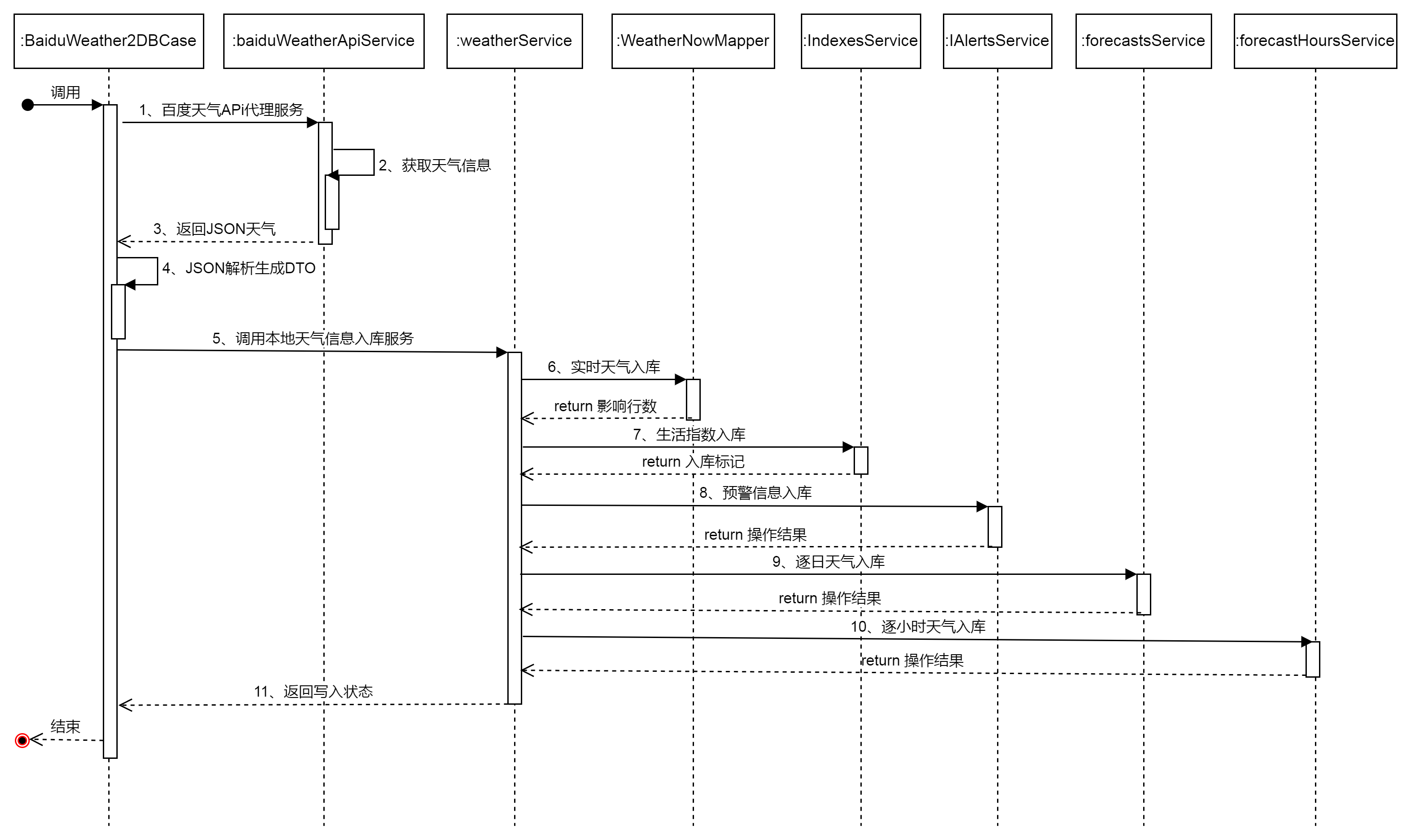
1、天气数据入库时序图
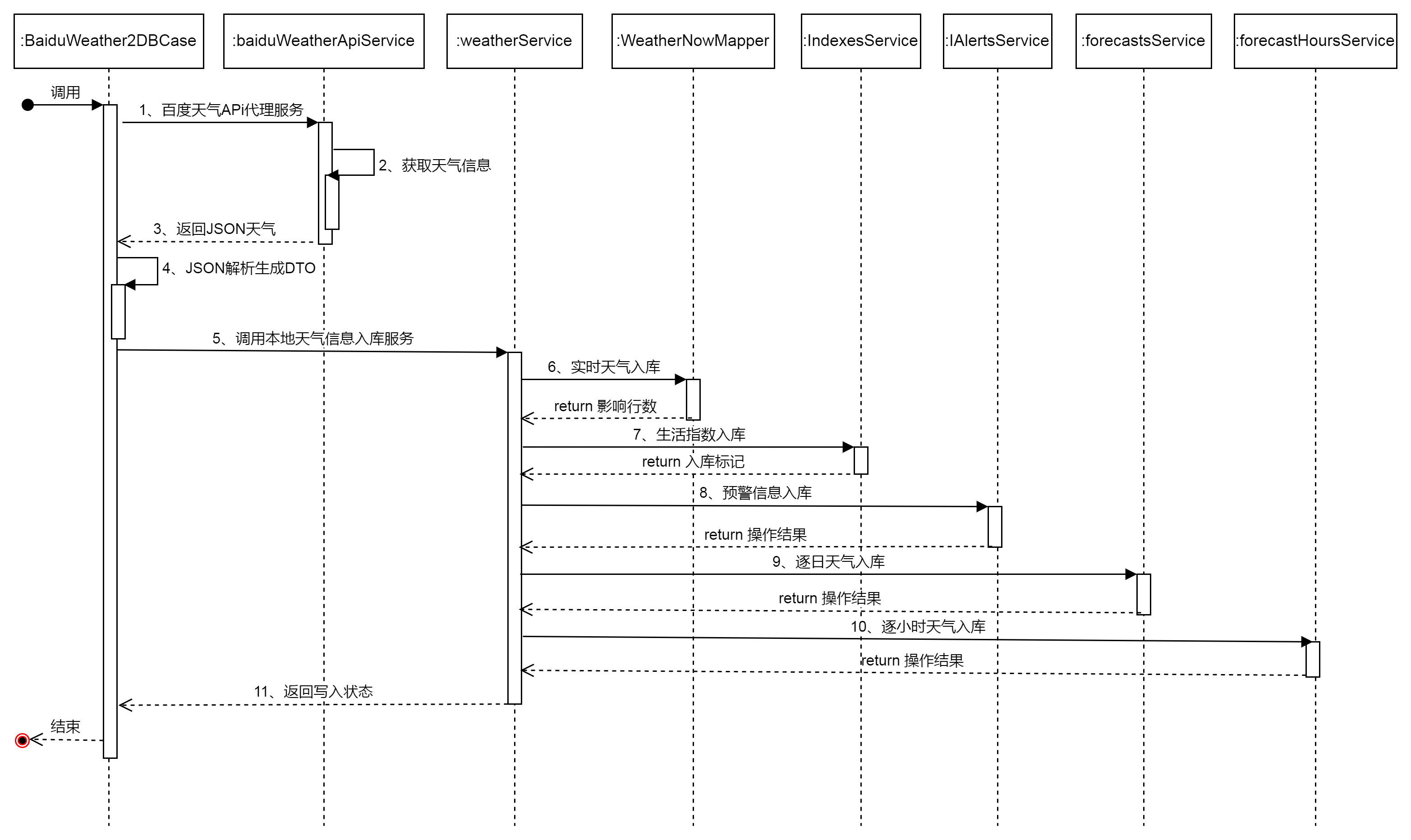
上图详细的展示了如何在可运行程序中集成百度接口,采用时序图的方式进行了详细交互过程的阐述。整个过程一共分为11个步骤,从入口程序调用开始,首先调用百度地图的接口,然后百度地图返回JSON结果,程序解析JSON反序列化成DTO的JavaBean,然后调用天气服务类,分别实现实时天气、预警信息、生活指数信息、逐日预报信息、逐小时预报信息的PG入库,最后返回写入状态。时序图在绘制时,为了美观在Service的名称上有一定省略,希望不影响阅读。
2、调用程序执行
关于MybatisPlus中涉及的Mapper、Service及其实现类在此不再进行赘述,通用的程序都比较简单,这里将核心的天气程序入口和持久化入口以及具体的天气信息入库方法在这里跟大家分享。入口核心程序如下所示:
package com.yelang.project.unihttp;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.IdWorker;
import com.burukeyou.uniapi.http.core.response.HttpResponse;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.yelang.project.thridinterface.BaiduWeatherApiServcie;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.BdWeatherDTO;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherInfoDTO;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherNowService;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class BaiduWeather2DBCase {
private static final String DATA_TYPE = "all";
@Autowired
private BaiduWeatherApiServcie baiduWeatherApiService;
@Autowired
private IWeatherNowService weatherService;
@Test
public void bdWeather2PG() {
String district_id = "430626";//表示具体的行政区划代号
HttpResponse<String> result = baiduWeatherApiService.getWeather(district_id, DATA_TYPE);
System.out.println(result.getBodyResult());
Gson gson = new Gson();
BdWeatherDTO bdWeatherInfo = gson.fromJson(result.getBodyResult(), BdWeatherDTO.class);
WeatherInfoDTO bdResult = bdWeatherInfo.getResult();
//将天气信息持久化到数据库中
if(null != bdResult) {
Long weatherId = IdWorker.getId();
bdResult.getWeatherNow().setPkId(weatherId);
bdResult.getWeatherNow().setLocationCode(district_id);
weatherService.insertWeatherInfo(bdResult);
}
}
}
为了实现天气数据的入库,在保存相关的生活指数信息、预警信息、逐日/小时天气预报信息时,我们还要将实时天气主键给相关的子表赋值,这里给出天气信息的持久化详细方法:
package com.yelang.project.weather.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.yelang.common.utils.StringUtils;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherAlerts;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherForecastHours;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherForecasts;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherIndexes;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherInfoDTO;
import com.yelang.project.weather.domain.WeatherNow;
import com.yelang.project.weather.mapper.WeatherNowMapper;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherAlertsService;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherForecastHoursService;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherForecastsService;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherIndexesService;
import com.yelang.project.weather.service.IWeatherNowService;
@Service
public class WeatherNowServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<WeatherNowMapper, WeatherNow> implements IWeatherNowService{
@Autowired
private IWeatherAlertsService alertsService;
@Autowired
private IWeatherForecastHoursService forecastHoursService;
@Autowired
private IWeatherForecastsService forecastsService;
@Autowired
private IWeatherIndexesService indexesService;
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,rollbackFor=Exception.class)
@Override
public void insertWeatherInfo(WeatherInfoDTO infoDto) {
WeatherNow now = infoDto.getWeatherNow();
//step1、保存实时天气信息
this.baseMapper.insert(now);
Long weatherId = now.getPkId();
//step2、保存生活指数信息
List<WeatherAlerts> alerts = infoDto.getAlerts();
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(alerts)) {
for(WeatherAlerts alert : alerts) {
alert.setWeatherPkId(weatherId);
}
alertsService.saveBatch(alerts);
}
//step3、保存预警信息
List<WeatherIndexes> indexes = infoDto.getIndexes();
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(indexes)) {
for(WeatherIndexes index : indexes) {
index.setWeatherPkId(weatherId);
}
indexesService.saveBatch(indexes);
}
//step4、保存天气预报
List<WeatherForecasts> forecasts = infoDto.getForecasts();
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(forecasts)) {
for(WeatherForecasts forecast : forecasts) {
forecast.setWeatherPkId(weatherId);
}
forecastsService.saveBatch(forecasts);
}
//step5、保存逐小时天气预报
List<WeatherForecastHours> forecastHours = infoDto.getForecastHours();
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(forecastHours)) {
for(WeatherForecastHours forecastHour : forecastHours) {
forecastHour.setWeatherPkId(weatherId);
}
forecastHoursService.saveBatch(forecastHours);
}
}
}
至此基本完成了调用程序和入口程序的编写,接下来在PG数据库中看一下实际的效果。
3、数据入库结果
执行以上程序可以在控制台中看到以下输出,说明正常的向PG数据库进行数据持久化。
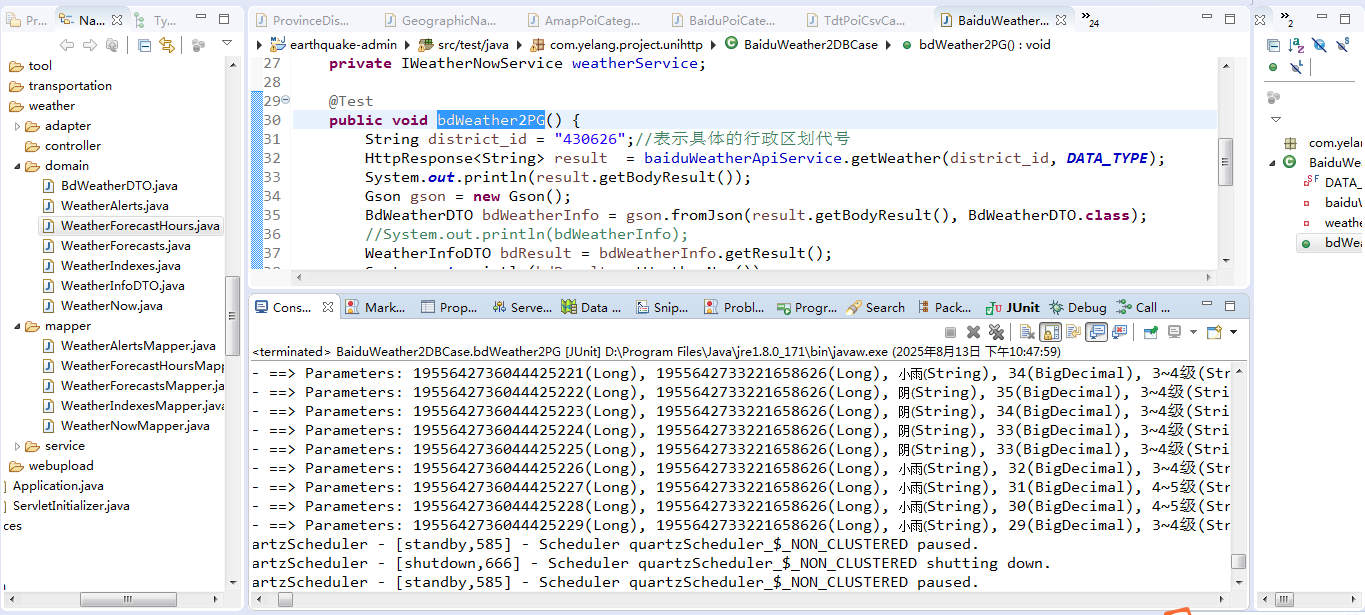
最后我们到数据库中查询一下是否将数据成功的写入,执行的SQL如下:
select * from biz_weather_now;
select * from biz_weather_alerts;
select * from biz_weather_forecasts
where weather_pk_id = 1955642733221658626;
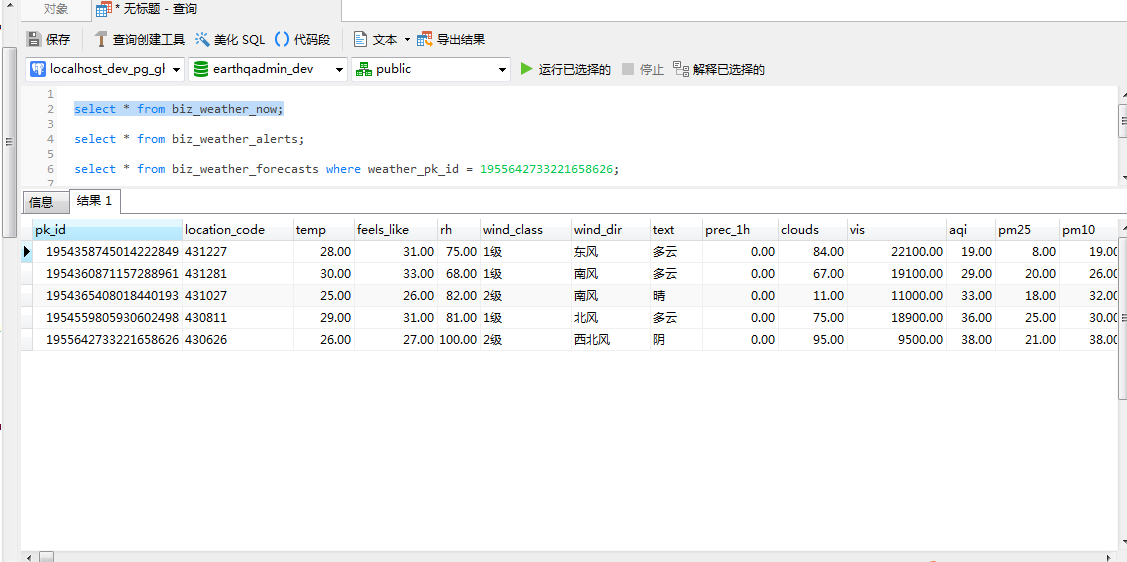
实时天气数据
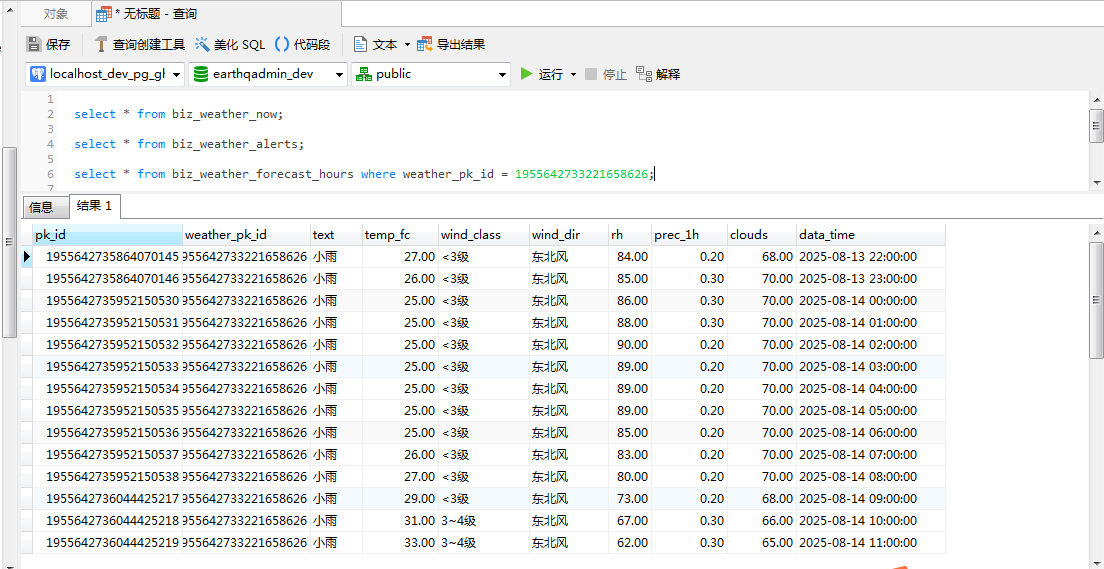
逐小时天气预报
四、总结
以上就是本文的主要内容,本文重点在于详细得介绍在MybatisPlus框架中如何将百度天气信息持久化到PG数据库中,首先介绍具体的PG数据库的设计与实现,然后详细介绍MybatisPlus的实体设计,最后以源代码的形式介绍如何将数据进行持久化,期待为大家提供一种良好的解决方案和参考。这一实践过程不仅涉及到技术层面的多种知识融合,如网络编程、JSON 数据处理、数据库操作以及框架应用等,还面临着诸如数据准确性、存储效率、系统稳定性等诸多挑战。通过对整个流程的深入研究和实践探索,我们希望能够为开发者提供一套完整、高效且可靠的解决方案,助力大家更好地利用百度天气数据,挖掘其潜在价值,同时也为类似的数据存储项目提供有益的参考和借鉴。行文仓促,定有许多的不足之处,欢迎各位朋友在评论区批评指正,不胜感激。
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心

评论前必须登录!
注册