引言
在NLua开发中,我们常面临一个重要选择:将C#函数注册到Lua环境调用,还是直接在Lua中实现逻辑? 直觉告诉我们,C#作为编译型语言性能更高,但跨语言调用的开销是否会影响整体性能?本文通过基准测试揭示真相。
测试场景
实现安全索引访问函数At,对比三种实现方式:
测试环境:
- .NET Framework 4.8.1
- Intel Core i7-1260P
- BenchmarkDotNet v0.15.0
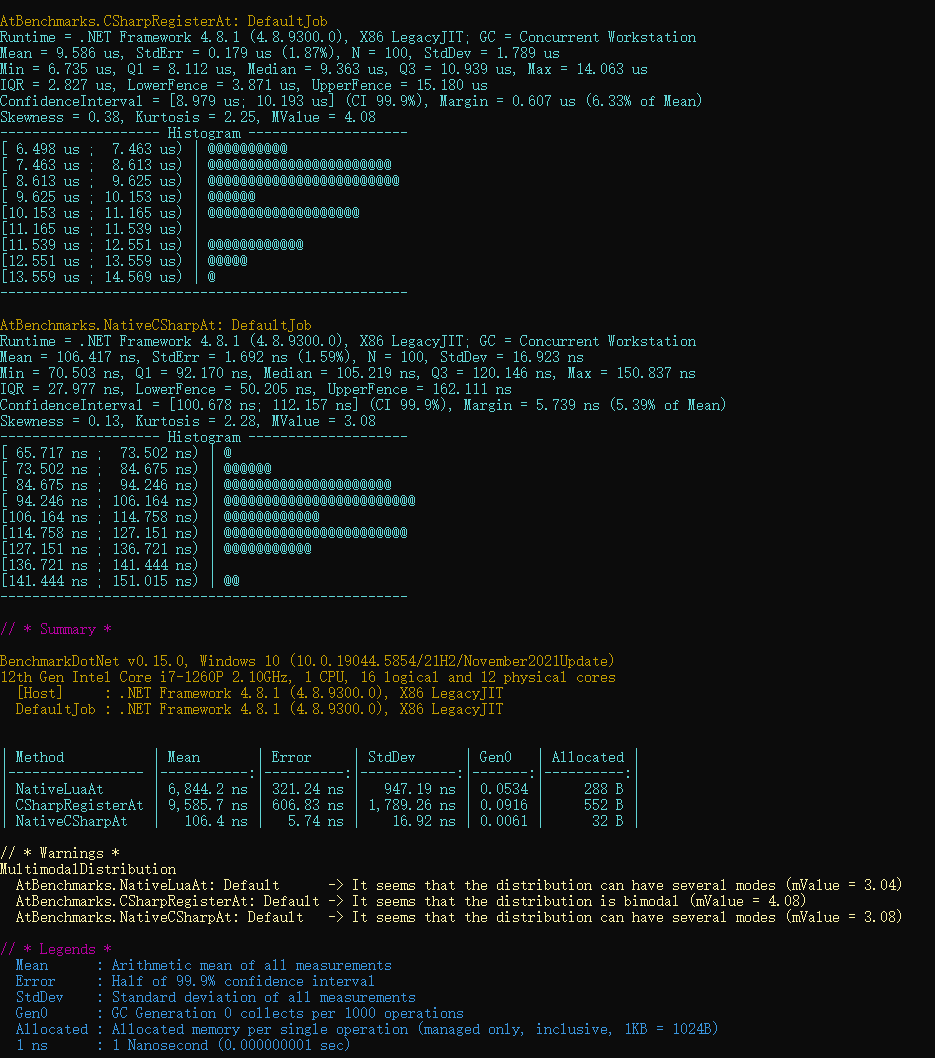
性能数据对比
| NativeLuaAt | 6,844 ns | 288 B |
| CSharpRegisterAt | 9,585 ns | 552 B |
| NativeCSharpAt | 106 ns | 32 B |
结论
出乎意料,直接在Lua中实现逻辑会更快,这里原因可能是将C#函数注册到Lua环境调用涉及到上下文切换等耗时动作。 相关代码见NLuaBenchmarkDotNetTest
代码
Lua代码
–[[
仅用于userdata索引访问函数,C#定义
参数:
tbl : 目标Lua表(数组形式)
index: 索引值(支持正负索引)
strict: [可选]严格模式,默认false,设为true时额外校验元素连续性
返回值:
对应索引位置的元素
异常:
类型错误或索引越界时抛出错误
–]]
function At(tbl, index)
— 参数校验阶段
— 检查第一个参数是否为table
if type(tbl) ~= "userdata" then
error("bad argument #1 (expected table, got "..type(tbl)..")", 2)
end
— 检查索引是否为整数
if type(index) ~= "number" or math.floor(index) ~= index then
error("index must be integer, got "..type(index), 2)
end
— 长度计算策略
local len = tbl.Length
— 严格模式下验证表连续性
— 索引转换逻辑
local adjusted_index
— 处理正索引(userdata是 的0-based)
if index >= 0 then
adjusted_index = index
— 处理负索引(从末尾倒数)
else
adjusted_index = len + index
end
— 边界检查与错误处理
— 有效索引范围:1 ≤ index ≤ len
if adjusted_index < 0 or adjusted_index >= len then
local direction = index >=0 and "positive" or "negative"
error(string.format("Index %d (%s) out of range [%d, %d]",
index, direction, –len, len–1), 2)
end
— 最终元素获取
return tbl[adjusted_index]
end
C#代码
/// <summary>
/// 安全索引访问器(支持Lua数组的0-based索引规则)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="collection">目标集合(支持IList接口的集合)</param>
/// <param name="index">索引值(支持负索引倒查)</param>
/// <param name="strict">严格模式校验元素连续性</param>
/// <returns>索引位置的元素</returns>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">输入集合为空</exception>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentException">集合类型不合法或索引无效</exception>
public static object At(IEnumerable collection, int index, bool strict = false)
{
// 参数基础校验
if (collection == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(collection), "输入集合不能为null");
// 类型安全转换
IList list = collection as IList;
if (list == null)
throw new ArgumentException("输入集合必须实现IList接口", nameof(collection));
// 获取有效长度
int count = list.Count;
if (count == 0)
throw new ArgumentException("集合中不包含有效元素", nameof(collection));
// 索引转换逻辑
int adjustedIndex = index >= 0 ? index : count + index;
// 边界校验
if (adjustedIndex < 0 || adjustedIndex >= count)
{
string msg = $"索引 {index} 超出有效范围 [{-count}, {count – 1}]";
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), msg);
}
// 严格模式校验
if (strict)
{
// 校验是否存在null元素
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (list[i] == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException($"严格模式检测到空元素 @ 位置 {i}");
}
}
}
return ConvertToDouble(list[adjustedIndex]);
}
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心






评论前必须登录!
注册