问题1:
有这样一道智力题:“某商店规定:三个空汽水瓶可以换一瓶汽水。小张手上有十个空汽水瓶,她最多可以换多少瓶汽水喝?”答案是5瓶,方法如下:先用9个空瓶子换3瓶汽水,喝掉3瓶满的,喝完以后4个空瓶子,用3个再换一瓶,喝掉这瓶满的,这时候剩2个空瓶子。然后你让老板先借给你一瓶汽水,喝掉这瓶满的,喝完以后用3个空瓶子换一瓶满的还给老板。如果小张手上有n个空汽水瓶,最多可以换多少瓶汽水喝?(汽水瓶)
输入、输出要求:
输入文件最多包含10组测试数据,每个数据占一行,仅包含一个正整数n(1<=n<=100),表示小张手上的空汽水瓶数。n=0表示输入结束,你的程序不应当处理这一行。
对于每组测试数据,输出一行,表示最多可以喝的汽水瓶数。如果一瓶也喝不到,输出0。
输入输出示例:
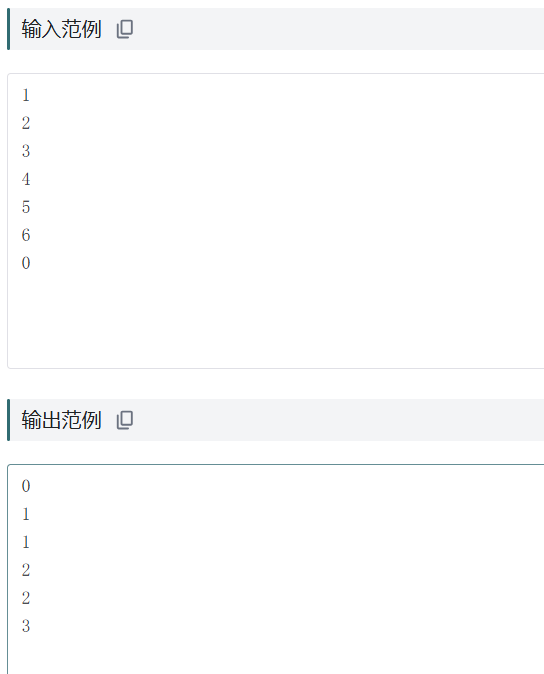
个人总结:
1.本题有一定难度,需要注意有借瓶机制,就是剩2个空瓶子时,然后你让老板先借给你一瓶汽水,喝掉这瓶满的,喝完以后用3个空瓶子换一瓶满的还给老板。开始编程时我忽略了这类情况;
2.本题除每3空瓶换1瓶饮料循环之后,还需要判断如最后空瓶为2时,采用借瓶操作,饮料数+1;
实现代码如下示:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
int first_case = 1,count=0;
while ((cin >>n) && count<10 ){
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n<2) {cout<<0;first_case = 0;continue;}
if(first_case != 1) cout<<endl;
first_case = 0;
int n_b=n,zb=0;
while(n_b>=3){
int x=n_b/3;
zb=zb+x;
n_b=n_b%3;
n_b=n_b+x;
}
if (n_b == 2) {
zb += 1;
}
cout<<zb;
count++;
}
return 0;
}
问题2:
N的阶乘写作N!表示小于等于N的所有正整数的乘积。阶乘会很快的变大,如13!就必须用32位整数类型来存储,70!即使用浮点数也存不下了。你的任务是找到阶乘最后面的非零位。举个例子,5!=1*2*3*4*5=120所以5!的最后面的非零位是2,7!=1*2*3*4*5*6*7=5040,所以最后面的非零位是4。
输入、输出要求:
一个不大于1000的整数N。
共一行,输出N!最后面的非零位。
输入输出示例:
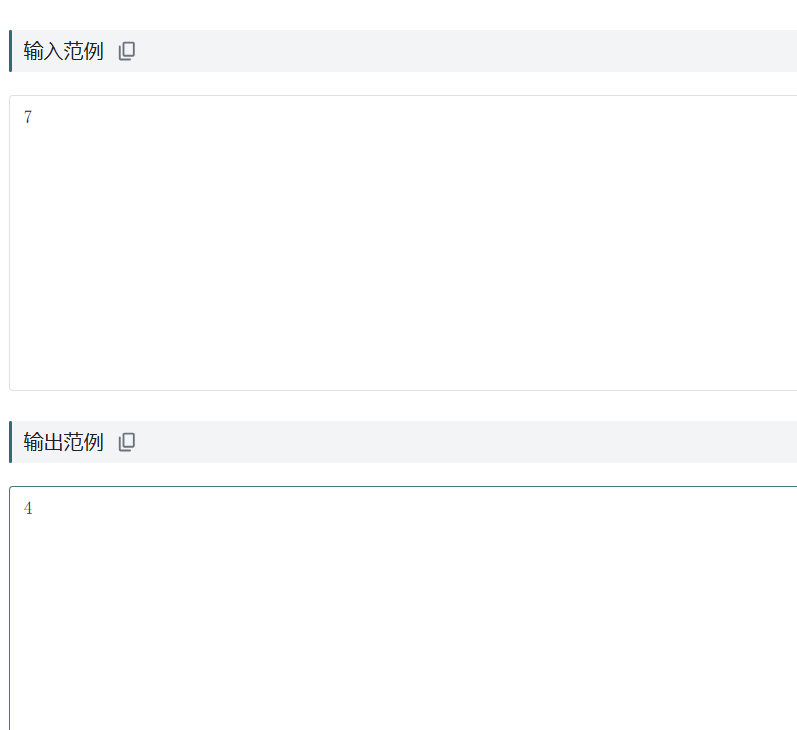
个人总结:
1.本题相对简单,注意阶乘结果递增迅速,需要注意越界问题,所以我采用的是当阶乘结果尾数为0时对阶乘除10,重复操作直到位数非0,为进一步防止越界再对结果%1000,将结果控制在三位数内;
实现代码如下示:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N;
cin>>N;
int count=1;
for(int i=2;i<=N;i++){
count=count*i;
while(count%10==0){
count=count/10;
}
count=count%1000;
}
cout<<count%10;
return 0;
}
问题3:
妈妈每天都要出去买菜,但是回来后,兜里的钱也懒得数一数,到底花了多少钱真是一笔糊涂帐。现在好了,作为好儿子(女儿)的你可以给她用程序算一下了。
输入、输出要求:
输入含有一些数据组,第一行第一个数是测试组数,第二行第一个数据是菜种数,每组数据包括菜种(字串),数量(计量单位不论,一律为double型数)和单价(double型数,表示人民币元数),因此,每组数据的菜价就是数量乘上单价啊。菜种、数量和单价之间都有空格隔开的。
注意样例输入应是如下:
1
3
青菜 1 2
罗卜 2 1.5
鸡腿 2 4.2
支付菜价的时候,由于最小支付单位是角,所以总是在支付的时候采用四舍五入的方法把分头去掉。所以,请输出一个精度为角的菜价总量。
输入输出示例:
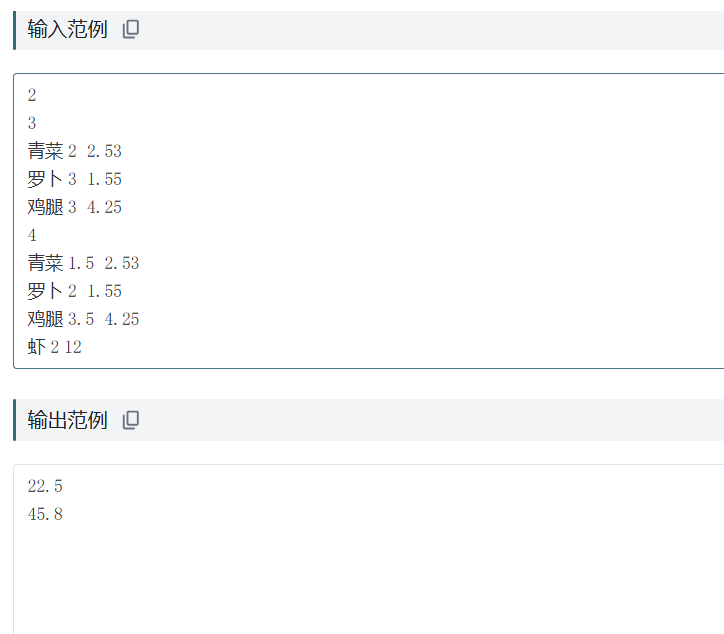
个人总结:
1.本题相对简单,控制好接受输入数据行数以及输出数据的精度换行操作即可。
实现代码如下示:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N;
cin>>N;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
int n;
cin>>n;
double zprice=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
string name;
double weight,price;
cin>>name>>weight>>price;
zprice=zprice+weight*price;
}
cout<<fixed << setprecision(1)<<zprice<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
专业TOPIC翻译打卡:
译文:
P1 人工智能领域的大部分研究,都可以被概括为构建能表现出智能行为的主体,这意味着主体执行器的动作必须是对其传感器所接收数据的理性响应。对应地,我们可以通过分析这些响应的不同层级,来对这类研究进行分类。
P2 最简单的响应是反射动作,即对输入数据的一种预设性反应。要实现更 “智能” 的行为,就需要更高层级的响应。例如,我们可以为主体赋予环境相关的知识,并要求它据此调整自身行为。投棒球的动作在很大程度上是一种反射动作,但决定如何、向何处投球则需要对当前环境的认知。如何存储、更新、访问这些现实世界的知识,并最终将其应用到决策过程中,至今仍是人工智能领域的一大挑战。
P3 如果我们希望主体追求某个目标(比如赢得一盘国际象棋,或是在拥挤的通道中穿行),就需要更高层级的响应能力。这种目标导向行为要求主体的响应(或一系列响应)是通过刻意制定行动计划,或是从当前选项中选择最优动作而产生的。
原文:
Much of the research in artificial intelligence can be characterized in the context of building agents that behave intelligently, meaning that the actions of the agent's actuators must be rational responses to the data received through its sensors. In turn, we can classify this research by considering different levels of these responses.
The simplest response is a reflex action, which is merely a predetermined response to the input data. Higher levels of response are required to obtain more "intelligent" behavior. For example, we might empower an agent with knowledge of its environment and require that the agent adjust its actions accordingly. The process of throwing a baseball is largely a reflex action but determining how and where to throw the ball requires knowledge of the current environment. How such real-world knowledge can be stored, updated, accessed, and ultimately applied in the decision-making process continues to be a challenging problem in artificial intelligence.
Another level of response is required if we want the agent to seek a goal such as winning a game of chess or maneuvering through a crowded passageway. Such goal-directed behavior requires that the agent's response, or sequence of responses, be the result of deliberately forming a plan of action or selecting the best action among the current options.
专业名词:
actuators 执行器
sensors 传感器
reflex action 反射动作
decision-making process 决策过程
goal-directed behavior 目标导向行为
passageway 通道;走廊(在 AI 语境中特指机器人穿行的空间)
current options 当前选项(在算法决策中特指可选择的动作集合)
maneuver (在 AI 语境中)操控;机动
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心



评论前必须登录!
注册