路由的基本使用步骤分为以下4步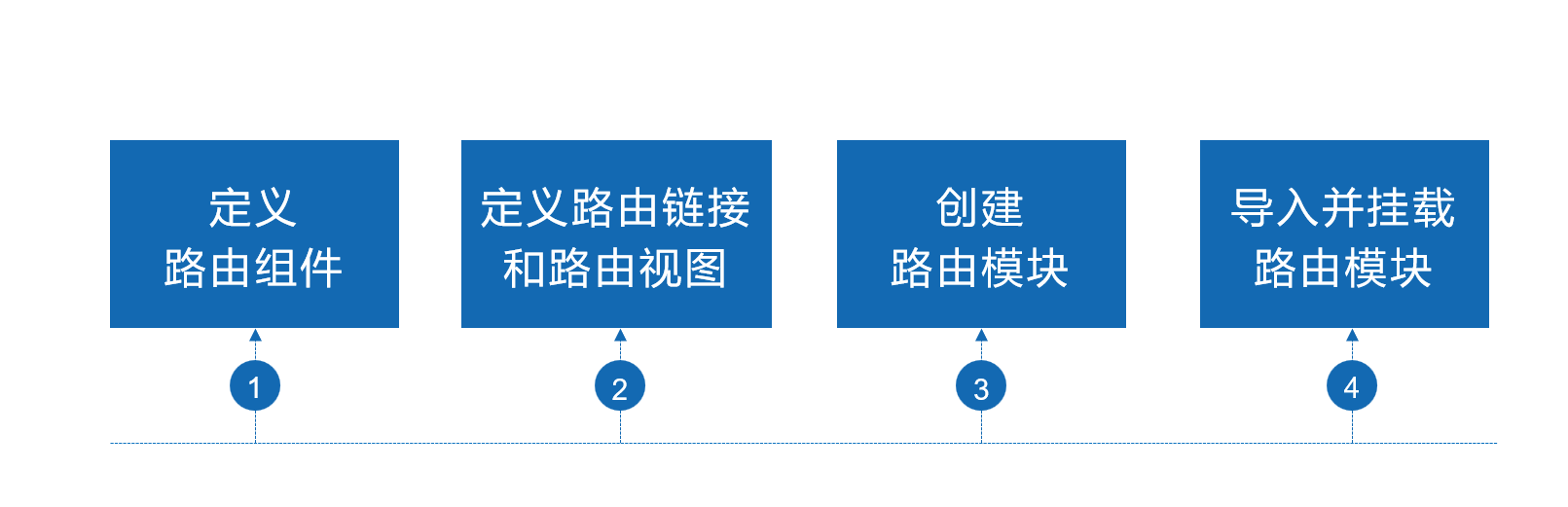
第一步:定义路由组件:略
第二步:定义路由链接和路由视图:
<template>
<div class="app-container">
<h1>App根组件</h1>
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<hr>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
我们演示项目的定义路由链接与路由视图如下:
<template>
<div class="home_container">
<el-container>
<!–头部 start–>
<el-header class="top-header">
<el-text class="home_title">东软云医院HIS系统</el-text>
<div class="home_userinfoContainer" >
<el-dropdown @command="handleCommand">
<el-button type="primary">
<el-avatar size="small" style="margin-right:10px ;"
src="https://cube.elemecdn.com/0/88/03b0d39583f48206768a7534e55bcpng.png" />
{{userStore.getUserInfo.value.realName}}<el-icon class="el-icon–right"><arrow-down /></el-icon>
</el-button>
<template #dropdown>
<el-dropdown-menu>
<el-dropdown-item command="" >我的设置</el-dropdown-item>
<el-dropdown-item command="logout">退出登录</el-dropdown-item>
</el-dropdown-menu>
</template>
</el-dropdown>
</div>
</el-header>
<!–头部 end–>
<el-container>
<!–左侧边栏 start –>
<el-aside width="200px" >
<el-menu
default-active="2"
class="el-menu-vertical-demo"
router @select="addTab" style="height: 700px">
<el-menu-item>
<el-icon><document /></el-icon><el-text class="mx-1" size="large">{{menus.meta.title}}</el-text>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item v-for="(menu,index) in menus.children" :index="menu.path" :key="menu.path" >
<el-icon><document /></el-icon>{{menu.name}}
</el-menu-item>
</el-menu>
</el-aside>
<!–左侧边栏 end –>
<el-container>
<el-main class="main">
<el-tabs v-model="editableTabsValue" type="card" editable
@edit="handleTabsEdit" @tab-click="clickTag" >
<el-tab-pane
align="center"
:key="item.name"
v-for="(item, index) in editableTabs"
:label="item.title"
:name="item.name"
:route="item.route"
>
<router-view></router-view>
</el-tab-pane>
</el-tabs>
</el-main>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {computed, ref} from 'vue'
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router'
import { postReq } from '../utils/api'
import { useUserStore } from '../store/user.js'
//路由
const router = useRouter()
//获取用户仓库对象
const userStore=useUserStore()
const menus=router.options.routes.find(m=>m.role==userStore.getUserInfo.value.useType);
const editableTabsValue=ref('')
const editableTabs=ref([])
const tabIndex=ref(0)
//查找路径对应的路由
function findCompontByPath(path){
let a=menus.children.find(m=>m.path==path);
if (a) {
return a;
}
return null;
}
//打开新窗口
function clickTag(tag,e){
//console.log(tag.paneName)
router.push(tag.paneName)
}
function addTab(path){
if(path){
let componet=findCompontByPath(path)
if (componet) {
if (!editableTabs.value.find(t => t.name == componet.path)) {
editableTabs.value.push({
title: componet.name,
name: componet.path,
route: componet.path
});
}
editableTabsValue.value = componet.path;
router.push(componet.path);
}
}
}
function handleTabsEdit(targetName, action) {
if (action === 'remove') {
let tabs = editableTabs.value;
let activeName = editableTabsValue.value;
if (activeName === targetName) {
tabs.forEach((tab, index) => {
// console.log(tab.name, targetName, tab.name === targetName);
if (tab.name === targetName) {
let nextTab = tabs[index + 1] || tabs[index – 1];
if (nextTab) {
activeName = nextTab.name;
}
}
});
}
editableTabsValue.value = activeName;
editableTabs.value = tabs.filter(tab => tab.name !== targetName);
router.push(activeName);
}
}
function handleCommand(command){
postReq("/user/logout").then(resp=>{
if(resp.data.result){
userStore.logOut();
router.push("/login")
}
})
}
</script>
<style>
.home_container {
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
width: 100%;
}
.top-header{
background-color: #20a0ff;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.left-aside{
background-color: #ECECEC;
}
.main{
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
color: #000;
text-align: left;
}
.home_title {
color: #fff;
font-size: 22px;
display: inline;
}
.home_userinfo {
color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
}
.home_userinfoContainer {
display: inline;
margin-right: 20px;
text-align: right;
}
</style>
在 Vue Router 中,<router-view></router-view> 组件的内容变化是基于当前的路由匹配结果。
路由匹配与视图渲染的工作原理
路由配置:Vue Router 的路由配置存储在 router.options.routes 中,您的代码通过 menus=router.options.routes.find(m=>m.role==userStore.getUserInfo.value.useType) 来获取当前用户角色对应的路由配置。
动态路由切换:
- 当用户点击左侧菜单的菜单项时,addTab 方法会被触发
- 该方法会根据路径找到对应的路由组件
- 如果该路由尚未在标签页中打开,则添加一个新标签页
- 然后通过 router.push(componet.path) 触发路由切换
标签页点击事件:
- 当用户点击标签页时,clickTag 方法会被触发
- 该方法同样通过 router.push(tag.paneName) 触发路由切换
标签页关闭事件:
- 当用户关闭标签页时,handleTabsEdit 方法会被触发
- 如果关闭的是当前激活的标签页,会自动切换到下一个或上一个标签页
- 同样通过 router.push(activeName) 来更新当前路由
视图更新:
- 当路由发生变化时,Vue Router 会自动查找与当前路径匹配的组件
- 然后将匹配到的组件渲染到 <router-view></router-view> 组件所在的位置
- 这就是为什么您的代码中,每个标签页的内容都是 <router-view></router-view>,但显示的内容却不同
关键逻辑分析
在您的代码中,路由切换的核心逻辑是通过以下几个方法实现的:
- addTab(path):当用户点击左侧菜单时,添加标签页并切换路由
- clickTag(tag,e):当用户点击标签页时,切换到对应的路由
- handleTabsEdit(targetName, action):当用户关闭标签页时,更新当前激活的标签页并切换路由
这些方法都通过 router.push() 来触发路由切换,而 <router-view></router-view> 会根据当前的路由自动渲染匹配的组件。
第三步:创建路由模块:
import {createRouter, createWebHistory, createWebHashHistory} from 'vue-router'
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue'
import { useUserStore } from '../store/user.js'
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(), // history 模式
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Login',
role:0,
component: defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/Login.vue`)),
meta: {title: 'Login'}
},
{
path: '/login',
name: 'Login',
role:0,
component: defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/Login.vue`)),
meta: {title: 'Login'}
},
{
path:'/home',
name:'系统信息',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/home.vue`)),
role:170,
meta: {title: '系统信息'},
children:[
{
path:'/constant',
name:'常数类别管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Constant.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/constantitem',
name:'常数项管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/ConstantItem.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/department',
name:'科室管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Department.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/user',
name:'账户管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/User.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/registlevel',
name:'挂号级别管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/RegistLevel.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/settlecategory',
name:'结算级别管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/SettleCategory.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/disecategory',
name:'疾病分类管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/DiseCategory.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/disease',
name:'诊断目录管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Disease.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/expense',
name:'费用科目表',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/ExpenseClass.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/fmeditem',
name:'非药品收费项目',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Fmeditem.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/rule',
name:'排班规则',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Rule.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/scheduling',
name:'排班计划',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neusys/Scheduling.vue`)),
}
]
},
{
path: '/home',
name: '挂号收费',
role:171,
component: defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/home.vue`)),
meta: {title: '挂号收费'},
children:[
{
path:'/customer',
name:'用户管理',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neureg/Customer.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/medicalcard',
name:'电子就诊卡',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neureg/MedicalCard.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/register',
name:'现场挂号',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neureg/Register.vue`)),
},
{
path:'/refund',
name:'退号',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neureg/Refund.vue`)),
}
]
},
{
path: '/home',
name: '门诊医生',
role:172,
component: defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/home.vue`)),
meta: {title: '门诊医生'},
children:[
{
path:'/docHome',
name:'门诊病历',
component:defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/neudoc/DocHome.vue`)),
}
]
},
]
})
// 全局路由守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// let userLogin = sessionStorage.getItem("userLogin");
const userStore = useUserStore()
// let isAuth=userStore.getUserInfo.value.isAuth;
let isAuth=userStore.getUserInfo.value.isAuth;
//判断路由的别名不是登录且未进行登录认证,就跳转去登录
if(to.name !== 'Login' && !isAuth){
next({ name: 'Login' })
}else if(to.name=="Login" && isAuth){
//已登录,不允许退回到登录页面
next({ path: '/home' })
}
else{
next()
}
})
router.afterEach((to, from)=>{
// console.log(to, from)
//console.log('afterEach')
})
export default router
上面我们是用懒加载的方式哟:
{
path: '/',
name: 'Login',
role:0,
component: defineAsyncComponent(() => import(`../components/Login.vue`)),
meta: {title: 'Login'}
},
命名路由
{ path: '路由路径', name: '路由名称', component: 组件 }
在定义路由匹配规则时,使用name属性为路由匹配规则定义路由名称,即可实现命名路由。当路由匹配规则有了路由名称后,在定义路由链接或执行某些跳转操作时,可以直接通过路由名称表示相应的路由,不再需要通过路由路径表示相应的路由。
我们通过如下方式使用它:
router.push(activeName); // activeName为路由名称
而且还有路由嵌套。
第四步:导入且挂载路由模块:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import router from './router'
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus';
import 'element-plus/theme-chalk/index.css';
import App from './App.vue'
import Axios from 'axios'
const app=createApp(App)
app.use(router)
app.use(createPinia())
app.use(ElementPlus)
app.mount('#app')
编程式导航
Vue Router提供了useRouter()函数,使用它可以获取全局路由实例,该全局路由实例中提供了常用的push()方法、replace()方法和go()方法,获取全局路由实例的示例代码如下。

push方法:
push()方法会向历史记录中添加一个新的记录,以编程方式导航到一个新的URL。当用户单击浏览器后退按钮时,会回到之前的URL。push()方法的参数可以是一个字符串路径,或者一个描述地址的对象,示例代码如下。
router.push('/about/tab1')// 字符串路径
router.push({ path: '/about/tab1' })// 带有路径的对象
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: '123'} })// 命名路由
router.push({ path: '/user', query: { id: '1' } })// 带查询参数,如:/user?id=1
router.push({ path: '/user', hash: '#admin' })// 带有Hash值,如:/user#admin
我们项目中也用到的 push:
function addTab(path){
if(path){
let componet=findCompontByPath(path)
if (componet) {
if (!editableTabs.value.find(t => t.name == componet.path)) {
editableTabs.value.push({
title: componet.name,
name: componet.path,
route: componet.path
});
}
editableTabsValue.value = componet.path;
router.push(componet.path);
}
}
}
导航守卫
·导航守卫用于控制路由的访问权限。例如,访问后台主页时,需要用户处于已登录状态,如果没有登录,则跳转到登录页面。用户在登录页面进行登录操作,若登录成功,则跳转到后台主页;若登录失败,则返回登录页面。
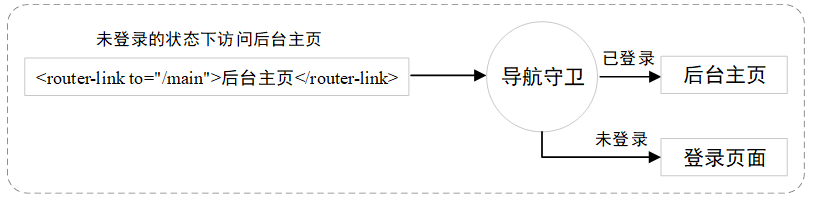
这里我们只介绍全局守卫,包括全局前置守卫beforeEach()和全局后置守卫afterEach(),在路由即将改变前和改变后进行触发。
// 全局路由守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// let userLogin = sessionStorage.getItem("userLogin");
const userStore = useUserStore()
// let isAuth=userStore.getUserInfo.value.isAuth;
let isAuth=userStore.getUserInfo.value.isAuth;
//判断路由的别名不是登录且未进行登录认证,就跳转去登录
if(to.name !== 'Login' && !isAuth){
next({ name: 'Login' })
}else if(to.name=="Login" && isAuth){
//已登录,不允许退回到登录页面
next({ path: '/home' })
}
else{
next()
}
})
全局路由守卫 beforeEach 详解
一、导航守卫的基本概念
在 Vue Router 中,导航守卫是一种拦截路由导航过程的机制,允许你在路由切换前后执行自定义逻辑。beforeEach是全局前置守卫,会在每次路由切换前被调用,是实现权限控制、登录验证等功能的核心机制。
二、beforeEach 守卫的参数解析
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// 守卫逻辑
})
- to: 即将要进入的目标路由对象
- from: 当前导航正要离开的路由对象
- next: 导航控制函数,必须调用此函数才能继续导航过程
三、next 函数的核心作用
next函数是导航守卫的关键控制接口,它的作用是决定路由导航的后续动作。必须调用 next () 才能让路由导航继续,否则导航会被阻塞。
根据调用方式的不同,next () 可以实现三种导航控制:
四、代码中的 next 函数应用场景
1. 未登录时重定向到登录页
if (to.name !== 'Login' && !isAuth) {
next({ name: 'Login' }) // 重定向到登录页
}
- 当目标路由不是登录页且用户未认证时
- 通过next({ name: 'Login' })重定向到登录路由
- 这会中断当前导航,开始向登录页的新导航
2. 已登录时禁止访问登录页
else if (to.name === 'Login' && isAuth) {
next({ path: '/home' }) // 重定向到首页
}
- 当用户已登录却尝试访问登录页时
- 通过next({ path: '/home' })重定向到首页
- 确保已登录用户不会看到登录界面
3. 允许正常导航
else {
next() // 允许导航继续
}
- 当导航符合条件(如已登录且访问非登录页)时
- 调用next()让导航过程继续,进入目标路由
五、next 函数的使用规则与注意事项
1. 必须调用 next ()
- 无论你想允许导航、阻止导航还是重定向,都必须调用 next ()
- 如果不调用 next (),导航将被永久阻塞,页面不会有任何反应
2. next () 的参数类型
| 无参数 | next() | 继续导航到目标路由 |
| 布尔值 | next(false) | 阻止导航,返回原路由 |
| 路由对象 | next({ path: '/login' }) | 重定向到指定路由 |
| 错误对象 | next (new Error (' 导航错误 ')) | 导航失败并触发错误处理 |
3. 调用时机与顺序
- 在守卫中可以有多个条件判断,但最终必须有一个 next () 被调用
- 多个全局守卫会按照注册顺序依次执行,每个守卫都必须调用 next () 才能继续
4. 异步场景处理
- 如果守卫中需要异步操作(如 API 请求验证),必须在异步操作完成后调用 next ()
- 示例:
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
try {
const userData = await fetchUserInfo()
if (userData.isAuth) {
next()
} else {
next({ name: 'Login' })
}
} catch (error) {
next(error)
}
})
六、实际开发中的最佳实践
权限控制:
- 在 beforeEach 中校验用户权限
- 对未授权用户重定向到登录页或提示错误
登录状态维护:
- 检查用户登录状态(如 token 有效性)
- 过期时强制重新登录
页面访问记录:
- 记录用户访问路径,用于历史回溯或行为分析
资源预加载:
- 在导航前预加载目标页面所需的数据或资源
next函数是 Vue Router 导航守卫的 "交通信号灯",通过控制它的调用方式,你可以精确管理路由导航的流程。
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心

![基于python的人脸检测识别录像系统[python]-计算机毕业设计源码+LW文档-网硕互联帮助中心](https://www.wsisp.com/helps/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/20260210120457-698b1ee9bfff8-220x150.jpg)

评论前必须登录!
注册