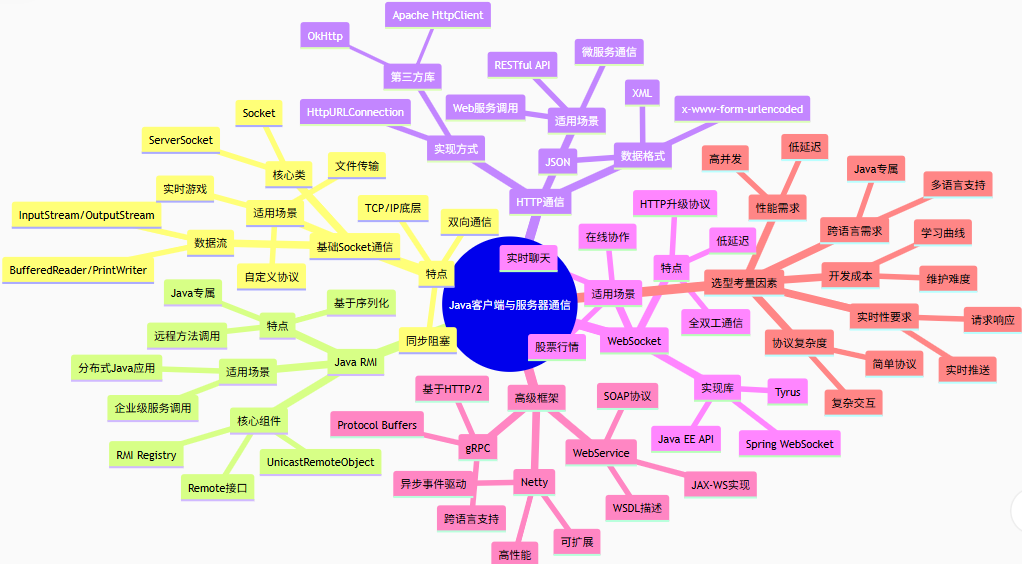
Java客户端与服务器通信
Java提供了多种方式来实现客户端与服务器之间的通信,下面我将介绍几种常见的方法:
1. 基于Socket的基本通信
服务器端代码
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class SimpleServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动,等待客户端连接…");
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("客户端已连接: " + clientSocket.getInetAddress());
// 获取输入输出流
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true);
// 通信循环
String inputLine;
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("收到客户端消息: " + inputLine);
out.println("服务器回复: " + inputLine);
}
// 关闭连接
in.close();
out.close();
clientSocket.close();
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端代码
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
// 获取输入输出流
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
// 发送消息
out.println("Hello, Server!");
// 接收回复
String response = in.readLine();
System.out.println("服务器回复: " + response);
// 关闭连接
out.close();
in.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. 使用Java RMI (远程方法调用)
RMI允许一个Java程序调用另一个Java虚拟机上对象的方法。
定义远程接口
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface RemoteService extends Remote {
String sayHello(String name) throws RemoteException;
}
实现远程服务
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.server.*;
public class RemoteServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteService {
public RemoteServiceImpl() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
public String sayHello(String name) throws RemoteException {
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
}
服务器端代码
import java.rmi.registry.*;
public class RMIServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
RemoteService service = new RemoteServiceImpl();
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Naming.rebind("RemoteService", service);
System.out.println("RMI服务已启动…");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端代码
import java.rmi.*;
public class RMIClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
RemoteService service = (RemoteService) Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost/RemoteService");
String response = service.sayHello("Client");
System.out.println("服务器回复: " + response);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. 使用HTTP通信 (HttpURLConnection)
客户端HTTP请求示例
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class HttpClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://example.com/api");
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 设置请求方法
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
// 获取响应
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("响应代码: " + responseCode);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
System.out.println("响应内容: " + response.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4. 使用第三方库 – Apache HttpClient
import org.apache.http.client.methods.*;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.*;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
public class ApacheHttpClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault()) {
HttpGet request = new HttpGet("http://example.com/api");
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request)) {
System.out.println("状态码: " + response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode());
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
System.out.println("响应内容: " + result);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5. WebSocket通信
服务器端 (使用Java EE或Spring)
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.*;
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket")
public class WebSocketServer {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session) {
System.out.println("客户端连接: " + session.getId());
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) {
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("服务器回复: " + message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session) {
System.out.println("客户端断开: " + session.getId());
}
}
客户端 (使用Java API)
import javax.websocket.*;
@ClientEndpoint
public class WebSocketClient {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session) {
System.out.println("连接已建立");
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("Hello, Server!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message) {
System.out.println("收到服务器消息: " + message);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebSocketContainer container = ContainerProvider.getWebSocketContainer();
try {
container.connectToServer(WebSocketClient.class,
URI.create("ws://localhost:8080/websocket"));
Thread.sleep(5000); // 保持连接一段时间
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
选择建议
简单通信:使用Socket或HttpURLConnection
分布式应用:考虑RMI或RPC框架
Web服务:使用HTTP客户端库
实时双向通信:WebSocket是更好的选择
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心


评论前必须登录!
注册