目录
表达式树技术解析与应用
一、学习表达式树的必要性
二、核心应用场景
动态技能系统
MOD支持系统
三、实战演示:属性获取器
传统模式缺陷
表达式树实现
条件触发系统
行为链组合
执行结果
运行时状态机
表达式树技术解析与应用
一、学习表达式树的必要性
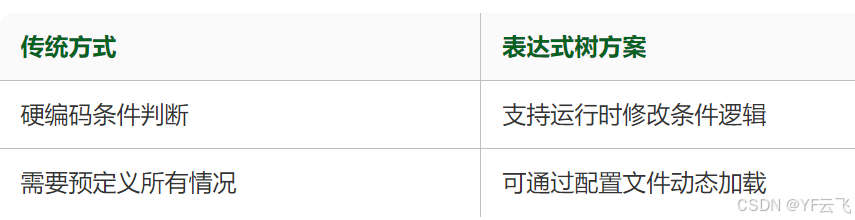
传统Unity开发存在三大核心痛点:
表达式树技术通过将代码转换为可操作的数据结构,提供以下优势:
- 运行时动态构建逻辑
- 实现组件间弱耦合通信
- 支持可视化配置游戏行为
二、核心应用场景
动态技能系统
- 通过JSON配置行为树
- 运行时解析生成表达式
- 实现无需重新编译的AI逻辑更新
MOD支持系统
- 支持玩家自定义逻辑脚本
- 在安全沙箱中运行表达式
- 实时加载玩家创作内容
三、实战演示:属性获取器
传统模式缺陷
public int GetPlayerStat(Player p, string statName)
{
switch(statName)
{
case "Health": return p.Health;
case "Mana": return p.Mana;
// 每新增属性需修改此处
}
}
表达式树实现
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using UnityEngine;
public class ExpressionTreeDemo : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
Player player = new () { Health = 100 };
Func<Player, int> healthProperty = CreatePropertyGetter<Player, int>("Health");
Debug.Log($"Player Health: {healthProperty(player)}");
}
public int GetPlayerStat(Player player, string statName)
{
Func<Player, int> propertyGetter = CreatePropertyGetter<Player, int>(statName);
return propertyGetter(player);
}
public Func<T, TProperty> CreatePropertyGetter<T, TProperty>(string propertyName)
{
ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "x");
MemberExpression property = Expression.Property(param, propertyName);
Expression<Func<T, TProperty>> lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<T, TProperty>>(property, param);
return lambda.Compile();
}
}
应用场景:动态获取对象属性 技术要点:属性访问表达式(Expression.Property)
条件触发系统
public class ConditionTrigger : MonoBehaviour
{
public string ConditionExpression = "Player.Health.CurrentHP < 0.3";
public GameObject ContextObject;
private Func<GameObject, bool> _compiledCondition;
private static Dictionary<string, Func<GameObject, bool>> _cache = new();
void Start()
{
if (!_cache.TryGetValue(ConditionExpression, out _compiledCondition))
{
var elements = ConditionExpression.Split('.');
var rootObj = Expression.Parameter(typeof(GameObject), "context");
Expression accessChain = rootObj;
foreach (var element in elements.Skip(1))
{
accessChain = Expression.PropertyOrField(accessChain, element);
}
var conditionExpr = BuildComparison(accessChain, "<", Expression.Constant(0.3f));
_compiledCondition = Expression.Lambda<Func<GameObject, bool>>(conditionExpr, rootObj).Compile();
_cache[ConditionExpression] = _compiledCondition;
}
}
void Update()
{
if (_compiledCondition(ContextObject))
{
Debug.Log("触发条件!");
}
}
private Expression BuildComparison(Expression left, string operatorStr, Expression right)
{
return operatorStr switch
{
"<" => Expression.LessThan(left, right),
">" => Expression.GreaterThan(left, right),
"==" => Expression.Equal(left, right),
"!=" => Expression.NotEqual(left, right),
"<=" => Expression.LessThanOrEqual(left, right),
">=" => Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(left, right),
_ => throw new NotSupportedException($"不支持的运算符: {operatorStr}")
};
}
}
应用场景:动态游戏事件触发
行为链组合
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using UnityEngine;
// 示例用法
public class ComboExample : MonoBehaviour
{
private ComboSystem _comboSystem;
void Start()
{
_comboSystem = new ComboSystem();
// 配置连招动作
_comboSystem.ActionExpressions.Add(GetComboExpression(typeof(AttackAnimation), nameof(AttackAnimation.Play), Expression.Constant("SwordSwing")));
_comboSystem.ActionExpressions.Add(GetComboExpression(typeof(EffectsManager), nameof(EffectsManager.Spawn), Expression.Constant("SwordHit")));
_comboSystem.ActionExpressions.Add(GetComboExpression(typeof(AttackAnimation), nameof(AttackAnimation.Play), Expression.Constant("SwordSwing2")));
_comboSystem.ActionExpressions.Add(GetComboExpression(typeof(DamageCalculator), nameof(DamageCalculator.Apply), Expression.Constant(new Vector3(0, 1, 0)), Expression.Constant(100f)));
// 执行连招
_comboSystem.ExecuteCombo();
}
Expression<Action> GetComboExpression(Type type, string methodName, params Expression[] args)
{
return Expression.Lambda<Action>(Expression.Call(type, methodName, null, args));
}
}
public class ComboSystem
{
public List<Expression<Action>> ActionExpressions = new();
public void ExecuteCombo()
{
var comboBlock = Expression.Block(
ActionExpressions.Select(exp => exp.Body)
);
var finalExpr = Expression.Lambda<Action>(comboBlock);
finalExpr.Compile().Invoke(); // 执行连招
}
}
// 示例动作类
public class AttackAnimation
{
public static void Play(string animationName)
{
Debug.Log($"播放动画: {animationName}");
}
}
public class EffectsManager
{
public static void Spawn(string effectName)
{
Debug.Log($"生成特效: {effectName}");
}
}
public class DamageCalculator
{
public static void Apply(Vector3 position, float damage)
{
Debug.Log($"应用伤害: {damage} 到位置: {position}");
}
}
执行结果
播放动画: SwordSwing
生成特效: SwordHit
播放动画: SwordSwing2
应用伤害: 100 到位置: (0.00, 1.00, 0.00)
关于 Expression.Block: Expression.Block 允许将多个表达式组合成一个块,并按顺序执行这些表达式。
运行时状态机
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
using UnityEngine;
using Object = UnityEngine.Object;
public class EnemyStateMachine : MonoBehaviour
{
// 状态评估器:根据敌人和英雄状态返回对应的行为函数
private Func<Enemy, Hero, Action<Enemy, Hero>> stateEvaluator;
private Action<Enemy, Hero> currentBehavior;
private Enemy enemy;
private Hero hero;
void Start()
{
enemy = FindObjectOfType<Enemy>();
hero = FindObjectOfType<Hero>();
stateEvaluator = CreateDynamicStateMachine();
}
void Update()
{
// 获取并执行当前行为
currentBehavior = stateEvaluator(enemy, hero);
currentBehavior(enemy, hero);
Debug.Log($"Enemy Aggression Level: {enemy.AggressionLevel}");
}
public Func<Enemy, Hero, Action<Enemy, Hero>> CreateDynamicStateMachine()
{
// 定义表达式参数
ParameterExpression enemyParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Enemy), "enemy");
ParameterExpression heroParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Hero), "hero");
// 创建条件表达式
BinaryExpression isHeroLowHealth = Expression.LessThan(
Expression.Property(heroParam, "Health"),
Expression.Constant(30)
);
BinaryExpression isHeroNearby = Expression.LessThan(
Expression.Property(heroParam, "Distance"),
Expression.Constant(10f)
);
Debug.Log($"Health Check: {isHeroLowHealth}");
Debug.Log($"Distance Check: {isHeroNearby}");
// 编译行为方法
var attackBehavior = CreateActionExpression("Attack").Compile();
var tauntBehavior = CreateActionExpression("Taunt").Compile();
var patrolBehavior = CreateActionExpression("Patrol").Compile();
// 构建行为选择逻辑
ConditionalExpression chooseTauntOrPatrol = Expression.Condition(
isHeroNearby,
Expression.Constant(tauntBehavior),
Expression.Constant(patrolBehavior)
);
ConditionalExpression finalDecision = Expression.Condition(
isHeroLowHealth,
Expression.Constant(attackBehavior),
chooseTauntOrPatrol
);
// 编译并返回状态机
var stateMachine = Expression.Lambda<Func<Enemy, Hero, Action<Enemy, Hero>>>(
finalDecision,
enemyParam,
heroParam
);
return stateMachine.Compile();
}
private Expression<Action<Enemy, Hero>> CreateActionExpression(string methodName)
{
ParameterExpression enemyParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Enemy), "enemy");
ParameterExpression heroParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Hero), "hero");
MethodInfo method = typeof(Enemy).GetMethod(methodName, new[] { typeof(Hero) });
MethodCallExpression methodCall = Expression.Call(enemyParam, method, heroParam);
return Expression.Lambda<Action<Enemy, Hero>>(methodCall, enemyParam, heroParam);
}
}
CreateDynamicStateMachine 方法说明: 1. 参数定义: – enemyParam: 敌人实例参数 – heroParam: 英雄实例参数
2. 条件检查: – 英雄生命值是否低于30 (heroLowHealth) – 英雄距离是否小于10单位 (heroNear)
3. 行为选择逻辑: – 优先检查英雄生命值,若低则执行攻击 – 其次检查距离,近距离时嘲讽,否则巡逻
CreateActionExpression 方法说明: 1. 创建方法调用表达式 2. 通过反射获取指定方法 3. 返回编译后的行为Lambda表达式
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心



评论前必须登录!
注册