目录
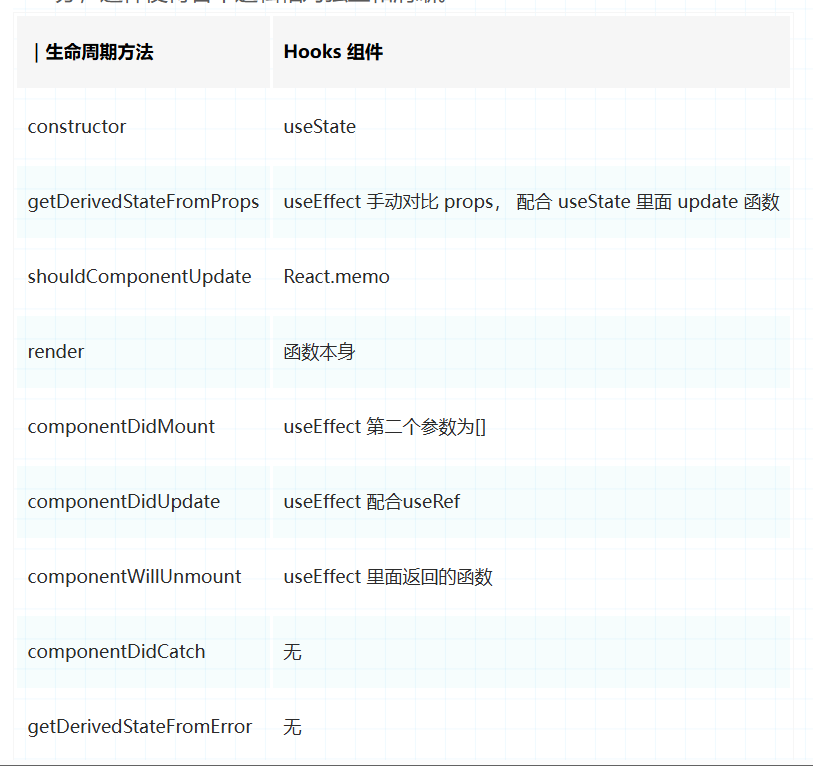
类式组件生命周期
函数式组件hook
组件通信
类组件和函数组件的区别
全局状态管理react-redux
路由
受控组件和非受控组件
高阶组件
Fiber
类式组件生命周期
constructor
初始化组件的状态和绑定事件处理器。
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this); // 绑定事件处理器
}
getDerivedStateFromProps
用于在挂载和更新前根据 props 更新 state。
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
if (nextProps.value !== prevState.value) {
return { value: nextProps.value };
}
return null;
}
render
必须实现的方法,渲染组件的虚拟 DOM。
componentDidMount
组件挂载完成后调用,通常用于发起网络请求、订阅事件等副作用操作。
componentDidMount() {
fetch('/api/data').then(response => this.setState({ data: response.data }));
}
shouldComponentUpdate
判断组件是否需要重新渲染。返回 false 可以阻止不必要的重新渲染。
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return nextState.count !== this.state.count;
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
在最新的渲染输出提交给 DOM 之前调用,可以捕获一些 DOM 信息(如滚动位置),以便在 componentDidUpdate 中使用。
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (prevProps.items.length < this.props.items.length) {
return this.listRef.scrollHeight;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate
组件更新完成后调用,可以在此进行副作用操作(如网络请求、DOM 操作等)
可以调用 setState(),但必须包裹在条件语句中,否则会导致无限循环
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
}
componentWillUnmount
组件卸载和销毁之前调用,通常用于清理工作,如取消请求、清除定时器、移除监听器等。
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timerID);
this.subscription.remove();
}
错误边界
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// 更新 state 以触发备用 UI 的渲染
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 你可以将错误日志上报给服务器
console.error("Uncaught error:", error, errorInfo);
}
函数式组件hook
useState
状态管理 返回一个状态值和更新函数
import React,{ useState } from 'react'
const [xxx, setXxx] = useState( )
useEffect
组合了 componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate 和 componentWillUnmount
useEffect(() => {
在return上面可以执行任何带副作用操作
return () => { 在组件卸载前执行
在此做一些收尾工作, 比如清除定时器/取消订阅等
}
}, [stateValue]) 如果指定的是[], 回调函数只会在第一次render()后执行
useLayoutEffect
用于在浏览器重新绘制屏幕之前触发

useContext
订阅React上下文
const value = useContext(MyContext);
// 1. 创建上下文
const ThemeContext = createContext('light');
// 2. 提供上下文
const App = () => (
<ThemeContext.Provider value="dark">
<Child />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
// 3. 使用上下文
const Child = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
return <div>Theme: {theme}</div>;
};
useRef
在函数组件中存储/查找组件内的标签或任意其它数据
const myRef = React.useRef()
function show(){
alert(myRef.current.value)
}
<input type="text" ref={myRef}/>
<button onClick={show}>点我提示数据</button>
useMemo 和 useCallback
相当于 shouldComponentUpdate 的优化,用于避免不必要的计算和渲染
useMemo 和 useCallback
useReducer
useReducer (redux)
useReducer 是 React Hooks 中的一个函数,用于管理和更新组件的状态。它可以被视为 useState 的一种替代方案,适用于处理更复杂的状态逻辑。
相比于 useState,useReducer 在处理复杂状态逻辑时更有优势,因为它允许我们将状态更新的逻辑封装在 reducer 函数中,并根据不同的动作类型执行相应的逻辑。这样可以使代码更具可读性和可维护性,并且更容易进行状态追踪和调试。
import { useReducer } from 'react';
const initialState = {
count: 0,
};
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement':
return { count: state.count – 1 };
default:
throw new Error('Unsupported action type');
}
};
function Counter() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
const increment = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'increment' });
};
const decrement = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'decrement' });
};
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {state.count}</p>
<button onClick={increment}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={decrement}>Decrement</button>
</div>
);
}
组件通信
父传子
//类式组件————父
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Son from './Son'
export default class Parent extends Component {
state = {
info: '我是父组件要传给子组件的数据!'
}
render() {
const { info } = this.state
return (
<div >
<h2>你好,我是Parent组件!</h2>
{/* 父组件通过在子标签中添加 属性=值 将数据传递给子组件 */}
<Son info={info} />
</div>
)
}
}
//子
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Son extends Component {
render() {
const { info } = this.props
return (
<div >
<h2>你好,我是Son组件!</h2>
<h3>我接受到父组件传递过来的数据是:{info}</h3>
</div>
)
}
}
//函数式组件————父
import React from 'react'
import Son from './Son'
export default function Parent() {
const info = '我是父组件要传给子组件的数据!'
return (
<div className='parent'>
<h2>你好,我是Parent组件!</h2>
{/* 父组件通过在子标签中添加 属性=值 将数据传递给子组件 */}
<Son info={info} />
</div>
)
}
//子
import React from 'react'
export default function Son(props) {
const {info} = props
return (
<div >
<h2>你好,我是Son组件!</h2>
<h3>我接受到父组件传递过来的数据是:{info}</h3>
</div>
)
}
子传父
//类式组件————父
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Son from './Son'
import './index.css'
export default class Parent extends Component {
state = {
info: '我是父组件要传给子组件的数据!'
}
changeInfo = (info) => {
this.setState({ info })
}
render() {
const { info } = this.state
return (
<div className='parent'>
<h2>你好,我是Parent组件!</h2>
{/* 父组件给子组件绑定一个回调函数changeInfo */}
<Son changeInfo={info => { this.changeInfo(info) }} />
<h3>info信息是:{info}</h3>
</div>
)
}
}
//子
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Son extends Component {
btnClick = () => {
const info2 = '我是子组件改变之后传给父组件的数据!'
this.props.changeInfo(info2 )
}
render() {
return (
<div className='son'>
<h2>你好,我是Son组件!</h2>
<button onClick={() => this.btnClick()}>点击改变父组件展示的info</button>
</div>
)
}
}
//函数式组件————父
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import Son from './Son'
import './index.css'
export default function Parent() {
const [info, setInfo] = useState('我是父组件要传给子组件的数据!')
function changeInfo(info) {
setInfo(info)
}
return (
<div className='parent'>
<h2>你好,我是Parent组件!</h2>
{/* 父组件给子组件绑定一个回调函数changeInfo */}
<Son changeInfo={info => changeInfo(info)} />
<h3>info信息是:{info}</h3>
</div>
)
}
//子
import React from 'react'
export default function Son(props) {
function btnClick() {
const info2 = '我是子组件改变之后传给父组件的数据!'
props.changeInfo(info2)
}
return (
<div className='son'>
<h2>你好,我是Son组件!</h2>
<button onClick={btnClick}>点击改变父组件展示的info</button>
</div>
)
}
非父子通信 context
//类式组件————祖组件
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Parent from './Parent'
import './index.css'
// 创建并暴露Context对象
export const { Provider, Consumer } = React.createContext()
export default class Grandpa extends Component {
state = { username: 'aDiao', age: 20 }
changeMessage = () => {
this.setState({ username: '啊叼', age: 18 })
}
render() {
const { username, age } = this.state
return (
<div className='grandpa'>
<h3>我是祖组件</h3>
<h4>我的用户名是:{username}</h4>
<h4>我的年龄是:{age}</h4>
<button onClick={this.changeMessage}>点我更改信息</button>
<Provider value={{ username, age }}>
<Parent />
</Provider>
</div>
)
}
}
//后代组件
import React, { Component } from 'react'
// 导入Grandpa组件中暴露出来的Context对象的Consumer
import { Consumer } from './Grandpa'
export default class Son extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Consumer>
{
(value) => {
return (<div className='son' >
<h3>我是子组件</h3>
<h4>我接收到的用户名是:{value.username}</h4>
<h4>我接收到的年龄是:{value.age}</h4>
</div >)
}
}
</Consumer >
)
}
}
//函数式组件————祖组件
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import Parent from './Parent'
import './index.css'
export const { Provider, Consumer } = React.createContext()
export default function Grandpa() {
const [user, setUser] = useState({ username: 'aDiao', age: 20 })
function changeMessage() {
setUser({
username: '啊叼',
age: 18
})
}
return (
<div className='grandpa'>
<h3>我是祖组件</h3>
<h4>我的用户名是:{user.username}</h4>
<h4>我的年龄是:{user.age}</h4>
<button onClick={changeMessage}>点我更改信息</button>
<Provider value={user}>
<Parent />
</Provider>
</div>
)
}
//后代组件
import React from 'react'
import { Consumer } from './Grandpa'
export default function Son() {
return (<div className='son' >
<h3>我是子组件</h3>
<h4>我接收到的用户名是:
<Consumer>
{value => {
return `${value.username}`
}}
</Consumer>
</h4>
<h4>我接收到的年龄是:
<Consumer>
{value => {
return `${value.age}`
}}
</Consumer></h4>
</div >)
}
发布订阅 pubsub
消息订阅与发布
类组件和函数组件的区别
类组件和函数式组件的区别
全局状态管理react-redux
redux
路由
路由
路由传参
受控组件和非受控组件
受控组件和非受控组件
高阶组件
至少满足下面一个条件
接受一个或者多个函数作为输入
输出一个函数
高阶组件
Fiber
React Fiber算法是React 16中引入的新的diff算法。之前的diff算法(即Stack Reconciler)是递归调用,在处理大量子元素时会导致栈溢出。
Fiber算法基于虚拟DOM树来对真实DOM树进行增量渲染。它将虚拟DOM树拆分成多个Fiber节点,每个Fiber节点维护自己的状态和子树。
Fiber解析
 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心

评论前必须登录!
注册