数据集:公开的World Happiness Report | Kaggle中的happiness dataset2017.
目标:基于GDP值预测幸福指数。(单特征预测)
代码:
文件一:prepare_for_traning.py
"""用于科学计算的一个库,提供了多维数组对象以及操作函数"""
from utils.features import prepare_for_training
"""数据预处理的一个私库"""
class LinearRegression:
def __init__(self,data,labels,polynomial_degree = 0,sinusoid_degree = 0,normalize_data = True):
"""
进行预处理操作
:param data:
:param labels:
:param polynomial_degree:
:param sinusoid_degree:
:param normalize_data:
"""
(data_processed,
features_mean,
features_deviation) = prepare_for_training(data,polynomial_degree = 0,sinusoid_degree = 0,normalize_data = True)
self.data = data_processed
self.labels = labels
self.features_mean = features_mean
self.features_deviation = features_deviation
self.polynomial_degree = polynomial_degree
self.sinusoid_degree = sinusoid_degree
self.normalize_data = normalize_data
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
self.theta = np.zeros((num_features,1))
""""数据,学习率,训练次数"""
def train(self,alpha,num_iterations = 500):
"""训练模块:梯度下降"""
cost_history = self.gradient_descent(alpha,num_iterations)
return self.theta,cost_history
def gradient_descent(self,alpha,num_iterations):
"""迭代模块"""
cost_history = []
for _ in range(num_iterations):
self.gradient_step(alpha)
cost_history.append(self.cost_function(self.data,self.labels))
return cost_history
def gradient_step(self,alpha):
"""
梯度下降参数更新算法,矩阵计算,使用小批量梯度下降算法
:param self:
:param alpha:
:return:
"""
num_examples = self.data.shape[0]
prediction = LinearRegression.hypothesis(self.data,self.theta)
delta = prediction – self.labels
theta = self.theta
theta = theta – alpha*(1/num_examples)*(np.dot(delta.T,self.data)).T
self.theta = theta
def cost_function(self,data,labels):
"""
损失计算模块
:param self:
:param data:
:param labels:
:return:
"""
num_examples = data.shape[0]
delta = LinearRegression.hypothesis(self.data,self.theta) – labels
cost = (1/2)*np.dot(delta.T,delta)/num_examples
"""print(cost.shape)"""
return cost[0][0]
"""装饰器"""
@staticmethod
def hypothesis(data,theta):
prediction = np.dot(data,theta)
return prediction
def get_cost(self,data,labels):
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,
self.polynomial_degree,
self.sinusoid_degree,
self.normalize_data
)[0]
return self.cost_function(data_processed,labels)
def predict(self,data):
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,
self.polynomial_degree,
self.sinusoid_degree,
self.normalize_data
)[0]
predictions = LinearRegression.hypothesis(data_processed,self.theta)
return predictions
文件2:Linear_regression.py
import numpy as np
"""用于科学计算的一个库,提供了多维数组对象以及操作函数"""
import pandas as pd
"""一个用于数据导入、导出、清洗和分析的库,本文中导入csv格式数据等等"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""pyplot提供了绘图接口"""
import matplotlib
"""一个强大的绘图库"""
# 设置matplotlib正常显示中文和负号
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei' # 指定默认字体为黑体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正确显示负号
from prepare_for_training import LinearRegression
data = pd.read_csv("D:/machine_learning/archive/2017.csv")
train_data = data.sample(frac = 0.8)
test_data = data.drop(train_data.index)
input_param_name = 'Economy..GDP.per.Capita.'
output_param_name = 'Happiness.Score'
x_train = train_data[[input_param_name]].values
y_train = train_data[[output_param_name]].values
x_test = test_data[[input_param_name]].values
y_test = test_data[[output_param_name]].values
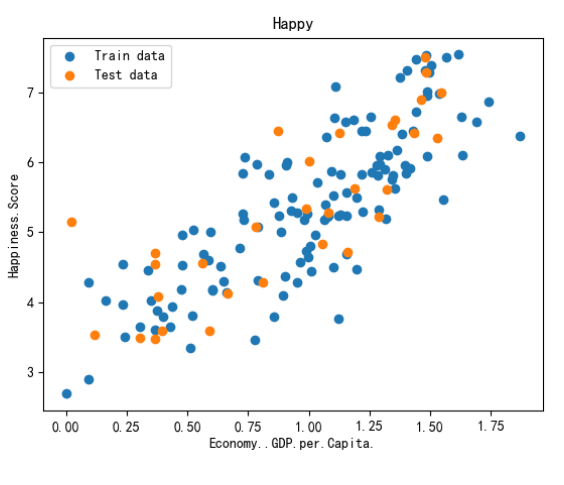
plt.scatter(x_train,y_train,label ='Train data')
plt.scatter(x_test,y_test,label ='Test data')
plt.xlabel(input_param_name)
plt.ylabel(output_param_name)
plt.title('Happy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
"""训练次数,学习率"""
num_iterations = 500
learning_rate = 0.01
linear_regression = LinearRegression(x_train,y_train)
(theta,cost_history) = linear_regression.train(learning_rate,num_iterations)
print('开始时的损失',cost_history[0])
print('训练后的损失',cost_history[-1])
plt.plot(range(num_iterations),cost_history)
plt.xlabel('Iter')
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.title('损失值')
plt.show()
predictions_num = 100
x_predictions = np.linspace(x_train.min(),x_train.max(),predictions_num).reshape(predictions_num,1)
y_predictions = linear_regression.predict(x_predictions)
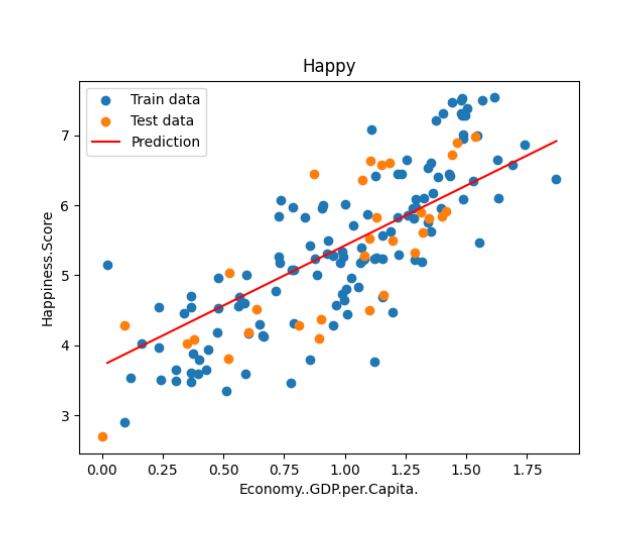
plt.scatter(x_train,y_train,label ='Train data')
plt.scatter(x_test,y_test,label ='Test data')
plt.plot(x_predictions,y_predictions,'r',label = 'Prediction')
plt.xlabel(input_param_name)
plt.ylabel(output_param_name)
plt.title('Happy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
效果图:


 网硕互联帮助中心
网硕互联帮助中心




评论前必须登录!
注册